 May 2003 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America”
May 2003 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America” Hair loss can be treated with medications like minoxidil and finasteride or surgery, but treatment effectiveness varies by alopecia type and accurate diagnosis is important.
 35 citations,
April 2013 in “Sexual medicine reviews”
35 citations,
April 2013 in “Sexual medicine reviews” 5-alpha reductase inhibitors slightly increase the risk of sexual and mood side effects, and breast growth in men.
 72 citations,
January 2011 in “Current Pharmaceutical Design”
72 citations,
January 2011 in “Current Pharmaceutical Design” S5αR inhibitors might help treat schizophrenia and other mental disorders but need more research.
 November 2023 in “International Journal of Medical Sciences”
November 2023 in “International Journal of Medical Sciences” New regenerative medicine-based therapies for hair loss look promising but need more clinical validation.
 209 citations,
September 2008 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
209 citations,
September 2008 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Androgens can both increase and decrease hair growth in different parts of the body.
 2 citations,
December 2004 in “Medicine”
2 citations,
December 2004 in “Medicine” Different hair and scalp disorders cause hair loss or excess hair growth, with various treatments available depending on the specific condition.
 41 citations,
April 2010 in “Gender Medicine”
41 citations,
April 2010 in “Gender Medicine” The conclusion is that hirsutism should be diagnosed and treated because it affects quality of life and may signal other health problems.
 May 2023 in “Scientific Reports”
May 2023 in “Scientific Reports” The seed extract of Lepidium sativum L. can potentially treat hair loss, showing effects similar to 5% minoxidil.
 3 citations,
February 2021 in “Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine”
3 citations,
February 2021 in “Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine” The Chinese herbal supplement BeauTop can potentially boost hair growth and thickness by increasing a protein called Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor.
 8 citations,
July 2012 in “Cambridge University Press eBooks”
8 citations,
July 2012 in “Cambridge University Press eBooks” Androgens can both increase body hair and cause scalp hair loss.
 26 citations,
February 2011 in “Anais Brasileiros De Dermatologia”
26 citations,
February 2011 in “Anais Brasileiros De Dermatologia” Polycystic Ovary Syndrome can cause hair loss and skin issues, and early treatment is important for preventing complications.
 229 citations,
August 2002 in “Experimental Gerontology”
229 citations,
August 2002 in “Experimental Gerontology” AGA causes hair loss by shrinking hair follicles due to DHT binding, and can be treated with finasteride and minoxidil.
 203 citations,
December 2004 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
203 citations,
December 2004 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Early diagnosis and treatment, using finasteride, minoxidil, or hair transplantation, improves hair loss outcomes.
June 2023 in “Journal of personalized medicine” Androgen treatment with dihydrotestosterone may help maintain height in patients with 5-α-reductase type 2 deficiency, especially before puberty.
 1 citations,
March 1954 in “Archives of dermatology”
1 citations,
March 1954 in “Archives of dermatology” Animal research has greatly advanced dermatology.
 25 citations,
November 2001 in “Kidney International”
25 citations,
November 2001 in “Kidney International” Male hormones worsen kidney transplant damage, but blocking them helps.
6 citations,
November 1977 in “Archives of Dermatology” A 6-year-old girl in the U.S. had a rare scalp infection caused by *Trichophyton soudanense*.
 4 citations,
August 2022 in “Lasers in medical science”
4 citations,
August 2022 in “Lasers in medical science” Both 1565-nm laser and 1064-nm laser safely and effectively reduce enlarged facial pores, with the 1064-nm laser causing fewer side effects.
 August 2020 in “Nigerian journal of paediatrics”
August 2020 in “Nigerian journal of paediatrics” A 24-month-old Nigerian girl developed early puberty with no family history, needing treatment her family couldn't afford.
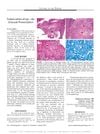 8 citations,
September 2016 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
8 citations,
September 2016 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” Enlarged sweat gland ducts may indicate scarring hair loss.
May 2023 in “MQRInvestigar” A young dog with an enlarged prostate and cysts improved significantly after treatment and surgery.
 March 2016 in “Reactions Weekly”
March 2016 in “Reactions Weekly” Post-finasteride syndrome causes various symptoms in men using finasteride, with no known cure.
 2 citations,
September 2012 in “Pharmaceutical patent analyst”
2 citations,
September 2012 in “Pharmaceutical patent analyst” European patent law now allows patents for new uses and dosages of known drugs, but protection scope is unclear.

Men with early balding may have a higher risk of prostate issues, and surgery for prostate cancer has a slight survival benefit over radiation.
4 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of zoo and wildlife medicine” Hormonal changes during the reproductive cycle may cause seasonal skin problems in captive female fossas.
 9 citations,
January 1981 in “Australian journal of biological sciences”
9 citations,
January 1981 in “Australian journal of biological sciences” Lambs fed a liquid diet showed abnormal wool and skin, which improved with more B-vitamins, suggesting a link to B-vitamin deficiency.
55 citations,
May 2007 in “Australasian journal of dermatology” Two boys developed a viral skin infection during chemotherapy, which resolved with improved immune function.
 December 2021 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
December 2021 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” Men with androgenetic alopecia, or hair loss, often have abnormal blood flow in their small blood vessels, which might be linked to inflammation and stress.
 July 2023 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology”
July 2023 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology” Reflectance confocal microscopy helped tell periorificial dermatitis apart from similar skin conditions.
 54 citations,
May 1998 in “Urology”
54 citations,
May 1998 in “Urology” Men with enlarged prostates often have more severe baldness.

























