 17 citations,
October 2012 in “Dermatologic clinics”
17 citations,
October 2012 in “Dermatologic clinics” Treating excessive hair in women requires a holistic approach, including medical, aesthetic, and emotional support.
 13 citations,
March 2011 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
13 citations,
March 2011 in “British Journal of Dermatology” A woman with scalp lymphoma and hair loss improved with radiotherapy, highlighting the need for biopsies in similar cases.
 10 citations,
February 2011 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
10 citations,
February 2011 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” The document concludes that proper diagnosis and evidence-based treatments are crucial for managing hair diseases, and psychological support for patients is important.
 9 citations,
January 2015 in “Springer eBooks”
9 citations,
January 2015 in “Springer eBooks” The document concludes that managing PCOS involves treating symptoms, regulating periods, and reducing health risks, with specific medications for fertility and metabolic issues.
 8 citations,
October 2017 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual”
8 citations,
October 2017 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual” A spermidine-based supplement may help hair grow longer by keeping it in the growth phase.
 6 citations,
July 2013 in “Acta Clinica Belgica”
6 citations,
July 2013 in “Acta Clinica Belgica” The document concludes that combination therapy is most effective for treating excessive hair growth in women with idiopathic hirsutism, and more research is needed to understand the condition.
 5 citations,
June 2015 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology”
5 citations,
June 2015 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology” Hirsutism, excessive hair growth in women, is often caused by PCOS and can be managed with medication and personalized treatment plans.
 5 citations,
June 2012 in “Journal of Cosmetic and Laser Therapy”
5 citations,
June 2012 in “Journal of Cosmetic and Laser Therapy” Finasteride and intense pulsed light effectively reduce unwanted facial hair in women, but may not be cost-effective.
 4 citations,
November 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology”
4 citations,
November 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology” The photographic method for measuring facial hair density is reliable and valid but needs further testing on different hair densities and skin colors.
 2 citations,
October 2018 in “Springer eBooks”
2 citations,
October 2018 in “Springer eBooks” Cancer treatments can cause skin-related side effects that may affect patient quality of life and require changes in treatment.
 2 citations,
January 2017 in “Cambridge University Press eBooks”
2 citations,
January 2017 in “Cambridge University Press eBooks” Manage PCOS in primary care with weight loss, psychological support, medication, and monitoring for health risks.
 1 citations,
May 2016 in “The Nurse Practitioner”
1 citations,
May 2016 in “The Nurse Practitioner” Treating PCOS is complex, involving medication like metformin and lifestyle changes, and requires attention to mental health due to high depression and anxiety rates.
 1 citations,
August 2013 in “Springer eBooks”
1 citations,
August 2013 in “Springer eBooks” Birth control pills and anti-androgen medications help manage hair growth, acne, and hair loss in women with PCOS.
 January 2023 in “Archives of Disease in Childhood Education & Practice”
January 2023 in “Archives of Disease in Childhood Education & Practice” Hirsutism in teens is often due to polycystic ovarian syndrome and needs careful assessment and support.

Microneedle technology is effective for skin rejuvenation and enhancing cosmeceutical delivery, with ongoing innovation and increasing commercialization.

Different scalp and hair disorders are more common in certain ethnic groups, with the most common being androgenetic alopecia, which is treated with medications like minoxidil and finasteride.
 July 2017 in “Contemporary Endocrinology”
July 2017 in “Contemporary Endocrinology” The document concludes that patient outcomes for Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia are often not ideal because of poor management and a need for better diagnosis and treatment methods.
January 2016 in “Dermatology Online Journal” Hormonal therapy changes skin and hair in transgender patients, who need better researched dermatologic care.
 November 2013 in “John Wiley & Sons, Ltd eBooks”
November 2013 in “John Wiley & Sons, Ltd eBooks” The document concludes that accurate diagnosis of male and female gonadal disorders is crucial for effective treatment and better patient outcomes.
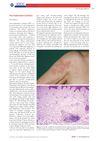 October 2012 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
October 2012 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Post-implantation erythema is a red skin condition after medical device implantation that sometimes goes away on its own.
November 2015 in “Springer eBooks” Laser hair removal can be effective for people with darker skin tones.
 61 citations,
July 2011 in “PLOS ONE”
61 citations,
July 2011 in “PLOS ONE” Spermidine may help reduce hair loss and deserves further testing as a treatment.
26 citations,
August 2008 in “Clinical endocrinology” The document concludes that more multidisciplinary research is needed to understand and treat PCOS, a condition that significantly affects women's health and quality of life.
16 citations,
April 2020 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual” Laser treatment can effectively reduce unwanted hair growth, particularly for people with fair skin and dark hair.
5 citations,
October 2017 in “JOGC/Journal of obstetrics and gynaecology Canada” The conclusion is that proper diagnosis and long-term treatment, including medication, hair removal, and lifestyle changes, are important for improving hirsutism, especially in PCOS patients.
 4 citations,
December 2022 in “Frontiers in Endocrinology”
4 citations,
December 2022 in “Frontiers in Endocrinology” Treating non-classic congenital adrenal hyperplasia is complex because the benefits of hormone treatment must be weighed against potential health risks.
 2 citations,
May 2013 in “The primary care companion for CNS disorders”
2 citations,
May 2013 in “The primary care companion for CNS disorders” A teenage girl's excessive hair growth was caused by a medication for mania, but improved after stopping the medication.
 January 2023 in “Skin appendage disorders”
January 2023 in “Skin appendage disorders” Low-dose oral minoxidil may help treat hair loss but is not FDA-approved and can cause side effects like unwanted hair growth and heart issues.
January 2022 in “Springer eBooks” 39 citations,
July 2005 in “Current medical research and opinion” Topical cream eflornithine 11.5% can slow hair growth and may help reduce hair removal frequency.























