 47 citations,
July 2013 in “Pharmacological Reviews”
47 citations,
July 2013 in “Pharmacological Reviews” Regenerative pharmacology, which combines drugs with regenerative medicine, shows promise for repairing damaged body parts and needs more interdisciplinary research.
 243 citations,
October 2003 in “Developmental biology”
243 citations,
October 2003 in “Developmental biology” Ectodin integrates BMP, SHH, and FGF signals in developing ectodermal organs.
 10 citations,
November 2010 in “Pigment Cell & Melanoma Research”
10 citations,
November 2010 in “Pigment Cell & Melanoma Research” Only skin melanocytes, not other types, can color hair in mice.
 November 2020 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
November 2020 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Ezh2 controls skin development by balancing signals for dermal and epidermal growth.
 45 citations,
October 2008 in “Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews”
45 citations,
October 2008 in “Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews” Activins and follistatins, part of the TGFβ family, are crucial for hair follicle development and skin health, affecting growth, repair, and the hair cycle.
 February 2024 in “Tissue & Cell”
February 2024 in “Tissue & Cell” New tissue engineering strategies show promise for regenerating human hair follicles, which could improve hair loss treatments.
 9 citations,
March 2023 in “Biomimetics”
9 citations,
March 2023 in “Biomimetics” New materials that better mimic natural skin structure could improve healing, especially for chronic wounds.
 31 citations,
September 2013 in “Stem Cells”
31 citations,
September 2013 in “Stem Cells” Smad1 and Smad5 are essential for hair follicle development and stem cell sleepiness.
 67 citations,
August 2007 in “American Journal of Pathology”
67 citations,
August 2007 in “American Journal of Pathology” Overexpressing the mineralocorticoid receptor in mouse skin causes skin thinning, early skin barrier development, eye issues, and hair loss.
Editing the FGF5 gene in sheep increases fine wool growth.
 24 citations,
October 2014 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine”
24 citations,
October 2014 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine” Genetic research has advanced our understanding of skin diseases, but complex conditions require an integrative approach for deeper insight.
 11 citations,
April 2013 in “SpringerPlus”
11 citations,
April 2013 in “SpringerPlus” Human skin's melanocytes respond to light by changing shape, producing pigments and hormones, which may affect sleep patterns.
 7 citations,
November 2013 in “Pediatric and Developmental Pathology”
7 citations,
November 2013 in “Pediatric and Developmental Pathology” Over half of the children had abnormal hair under a microscope, with many having genetic hair conditions.
 6 citations,
November 2018 in “Histochemistry and Cell Biology”
6 citations,
November 2018 in “Histochemistry and Cell Biology” Mongolian gerbils heal wounds differently than mice, with unique protein levels and gene expression that affect skin repair.
 4 citations,
August 2016 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
4 citations,
August 2016 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Using cetirizine on the skin and taking vitamin D can help increase hair growth in children with hair loss from ectodermal dysplasia.
 207 citations,
March 2012 in “Development”
207 citations,
March 2012 in “Development” Skin needs dermal β-catenin activity for hair growth and skin cell multiplication.
 39 citations,
January 2016 in “PubMed”
39 citations,
January 2016 in “PubMed” Understanding how EDC genes are regulated can help develop better drugs for skin diseases.
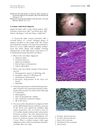 2 citations,
August 2010 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
2 citations,
August 2010 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” A 65-year-old woman has a growing bald spot on her scalp.
 52 citations,
June 1981 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
52 citations,
June 1981 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Oral retinoids are effective for severe skin conditions but require careful use due to side effects.
 17 citations,
December 2006 in “Gene Expression Patterns”
17 citations,
December 2006 in “Gene Expression Patterns” Scube3 gene affects mouse embryo growth in multiple areas, but needs more research.
 2 citations,
January 2013 in “Elsevier eBooks”
2 citations,
January 2013 in “Elsevier eBooks” The document explains the genetic causes and characteristics of inherited hair disorders.
 1 citations,
April 2016 in “CRC Press eBooks”
1 citations,
April 2016 in “CRC Press eBooks” Skin aging reflects overall body aging and can indicate internal health conditions.
 September 2021 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
September 2021 in “Research Square (Research Square)” Not having enough or having too much of the protein Grainyhead-like 3 leads to various developmental problems.
 99 citations,
June 2005 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
99 citations,
June 2005 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Hair ages due to genetics and environmental factors, leading to graying and thinning, with treatments available for some conditions.
 6 citations,
June 2021 in “Developmental biology”
6 citations,
June 2021 in “Developmental biology” Dermal EZH2 controls skin cell development and hair growth in mice.
 November 2020 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
November 2020 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Dermal EZH2 controls skin cell growth and differentiation in mice.
 January 2009 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2009 in “Springer eBooks” The document concludes that managing skin conditions during pregnancy is important and requires specialized care.
117 citations,
April 2008 in “Developmental biology” Ectodysplasin inhibits Wnt signaling to help form hair follicles.
 2 citations,
September 2021 in “Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases”
2 citations,
September 2021 in “Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases” People with hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia are more likely to experience long-term fatigue and hair loss after COVID-19.
 April 2024 in “Journal of translational medicine”
April 2024 in “Journal of translational medicine” Melanocytes are important for normal body functions and have potential uses in regenerative medicine and disease treatment.




























