5 citations,
January 2021 in “Indian Journal of Pharmacology” Nilotinib can cause generalized keratosis pilaris.
 12 citations,
July 2019 in “Acta Neurologica Belgica”
12 citations,
July 2019 in “Acta Neurologica Belgica” Levodopa for Parkinson's disease might be linked to skin issues like melanoma, but it's unclear if the drug or the disease causes them.
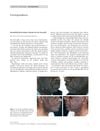 6 citations,
May 2012 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology”
6 citations,
May 2012 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology” Oral minoxidil can cause inflamed, ingrown hairs in the beard area.
 8 citations,
January 2009 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
8 citations,
January 2009 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” Finasteride can cause rare breast growth side effect, with varying recovery after stopping.
 39 citations,
April 2001 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
39 citations,
April 2001 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Latanoprost, a glaucoma medication, caused excessive eyelid hair growth in many patients.

The document is a detailed guide on skin conditions and treatments for dermatologists.
 12 citations,
December 1985 in “Dicp-The annals of pharmacotherapy”
12 citations,
December 1985 in “Dicp-The annals of pharmacotherapy” Carbamazepine can cause hair loss, which may reverse when the medication is stopped.
 33 citations,
August 1973 in “American Heart Journal”
33 citations,
August 1973 in “American Heart Journal” Propranolol can cause reversible hair loss.
21 citations,
July 2011 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” A man developed a rash similar to pityriasis rubra pilaris after starting sorafenib for cancer, possibly due to the drug's effect on skin cells.
 14 citations,
July 2016 in “Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology”
14 citations,
July 2016 in “Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology” Cedrol may prevent hair loss caused by chemotherapy better than minoxidil.







