 July 2004 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
July 2004 in “British Journal of Dermatology” The document concludes that accurate diagnosis and treatment are crucial in dermatology, and it presents various findings on skin conditions and treatments.

The document concludes that dermatology training and grading scales need to better represent dark-skinned individuals to improve diagnosis and assessment of skin conditions.
 September 2017 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
September 2017 in “Pediatric Dermatology” The document concludes that an experimental drug may help wound healing in Epidermolysis Bullosa, links Hydroa vacciniforme to EBV, discusses diagnosing hair loss disorders, finds many children with eczema have allergies, reviews the safety of a skin medication in children, notes side effects of a Duchenne's treatment, and identifies a marker for pediatric mastocytosis.
 May 2002 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
May 2002 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Finasteride is effective for male hair loss, teledermatology is accurate and accepted, and cyclosporin helps treat toxic epidermal necrolysis.
 37 citations,
January 1997 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
37 citations,
January 1997 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Hair problems are common and distressing for women, but increasing knowledge of treatments offers hope.
 10 citations,
March 2018 in “Anais Brasileiros De Dermatologia”
10 citations,
March 2018 in “Anais Brasileiros De Dermatologia” More hair loss leads to higher risk of psychosexual disorders, especially in women.
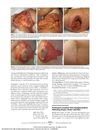 3 citations,
May 2010 in “Archives of dermatology”
3 citations,
May 2010 in “Archives of dermatology” Herpes zoster infection can cause permanent hair color change in the affected area.
 March 2012 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
March 2012 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Hair casts are often mistaken for head lice, scalp pain in hair loss is linked to certain nerve factors, eyelash growth treatment is safe and effective, and nail shedding in children may follow hand-foot-mouth disease.
 December 2012 in “Drugs & Therapy Perspectives”
December 2012 in “Drugs & Therapy Perspectives” Doctors use their experience to choose treatments for scarring hair loss because it's hard to diagnose and treat.
 June 2008 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
June 2008 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Herpes gestationis is linked to certain antigens, atopic eczema affects T cell populations and may be eased by breastfeeding, higher doses of anti-androgen treatment can improve androgenic alopecia, topical minoxidil increases hair thickness, long-term methotrexate therapy can cause liver fibrosis in psoriasis patients, and Lichen Sclerosus et Atrophicus patients aren't at higher risk for autoimmune disorders.
 28 citations,
November 2017 in “Skin appendage disorders”
28 citations,
November 2017 in “Skin appendage disorders” The document concludes that accurate diagnosis and treatment of scalp itch require differentiating between various conditions using a proposed five-step evaluation process.
 7 citations,
July 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
7 citations,
July 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy” During the COVID-19 pandemic in Turkey, the most common skin problem for both kids and adults was acne.
 6 citations,
February 2014 in “Human & experimental toxicology”
6 citations,
February 2014 in “Human & experimental toxicology” Testosterone injections can cause skin darkening and thickening.
 2 citations,
December 2021 in “Journal of Veterinary Medical Science”
2 citations,
December 2021 in “Journal of Veterinary Medical Science” Lokivetmab reduced itching in a dog with skin lymphoma.
 1 citations,
December 2021 in “Medical Records”
1 citations,
December 2021 in “Medical Records” The COVID-19 pandemic led to fewer dermatology visits, older and more male patients, and more stress-related skin issues.
 March 2024 in “Cirugía y Cirujanos (English Edition)”
March 2024 in “Cirugía y Cirujanos (English Edition)” Kidney transplant patients often have skin issues, mainly infections.
 January 2021 in “ACTA SCIENTIAE VETERINARIAE”
January 2021 in “ACTA SCIENTIAE VETERINARIAE” A dog with skin issues improved with prednisone after accurate diagnosis.
 May 2009 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
May 2009 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” Mast cells play a significant role in hair loss conditions like male pattern hair loss and alopecia areata.
 December 2016 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
December 2016 in “British Journal of Dermatology” The meeting highlighted the importance of genetic testing and multidisciplinary approaches in pediatric dermatology.
 101 citations,
July 2020 in “Dermatologic therapy”
101 citations,
July 2020 in “Dermatologic therapy” COVID-19 can cause skin issues like rashes and "COVID toes," and people with skin conditions should adjust their treatments if they get the virus.
 44 citations,
March 2020 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
44 citations,
March 2020 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” The pandemic has pushed dermatology education and care to adopt digital solutions, which are effective and likely to continue post-pandemic.
 5 citations,
February 2010 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
5 citations,
February 2010 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Treating both the mind and skin together, especially by managing stress, can greatly improve outcomes for skin disorders linked to psychological issues.

Genetic testing can help diagnose skin conditions but needs more research for full effectiveness.
 November 2019 in “Harper's Textbook of Pediatric Dermatology”
November 2019 in “Harper's Textbook of Pediatric Dermatology” The document is a detailed medical reference on skin and genetic disorders.
 June 2023 in “Revista médica hondureña”
June 2023 in “Revista médica hondureña” Most pediatric cancer patients in the study developed skin problems, often due to their cancer treatment.
 54 citations,
September 2005 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
54 citations,
September 2005 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Dermatologists are more accurate than general practitioners in diagnosing skin conditions, especially skin cancer.
 44 citations,
January 2002 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
44 citations,
January 2002 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Skin reactions to antidepressants are common but usually not serious and can be treated.
 39 citations,
June 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
39 citations,
June 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy” The COVID-19 pandemic led to an increase in untreated hair diseases and showed the importance of teledermatology.
 39 citations,
March 2003 in “The Veterinary clinics of North America. Small animal practice/Veterinary clinics of North America. Small animal practice”
39 citations,
March 2003 in “The Veterinary clinics of North America. Small animal practice/Veterinary clinics of North America. Small animal practice” Behavioral dermatology treats skin problems by considering both emotional and physical factors.
 23 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
23 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Permanent hair loss from cicatricial alopecia is treated by reducing inflammation and managing symptoms, but regrowth in scarred areas is unlikely.






























