 20 citations,
October 2003 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
20 citations,
October 2003 in “The Journal of Dermatology” DCP therapy causes side effects like weakness, flushing, headaches, and taste changes, but less frequently causes hypertension and diabetes.
48 citations,
June 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Contact sensitizers like DCP and SADBE are the most effective treatments for alopecia areata.
 14 citations,
September 2009 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
14 citations,
September 2009 in “International Journal of Dermatology” DCPA is a chronic leg infection often related to Staphylococcus aureus, affecting mostly young men in India.
11 citations,
January 2009 in “Indian journal of dermatology, venereology, and leprology” DCPA is a chronic skin condition affecting the lower limbs, mainly in men, with unclear causes and treatments that often don't work well.
 4 citations,
August 2013 in “Case reports in dermatology”
4 citations,
August 2013 in “Case reports in dermatology” A patient with total hair loss developed vitiligo after using a treatment called DCP.
1 citations,
January 2022 in “Skin appendage disorders” DCPA is a chronic skin condition affecting the legs, often misdiagnosed, and needs more research for better understanding and treatment.
 27 citations,
December 2015 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
27 citations,
December 2015 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Diphencyprone helped most patients with alopecia areata regrow some hair.
 27 citations,
May 2007 in “Archives of dermatological research”
27 citations,
May 2007 in “Archives of dermatological research” Diphencyprone treatment increases CD8 lymphocytes in the scalp, which is associated with hair regrowth in alopecia areata patients.
13 citations,
January 2014 in “Zhongguo zhongyao zazhi” Dendrobium candidum polysaccharides promote hair growth.
 9 citations,
April 2016 in “Australasian journal of dermatology”
9 citations,
April 2016 in “Australasian journal of dermatology” Combining imiquimod with diphenylcyclopropenone may improve treatment outcomes for alopecia areata patients who don't respond to diphenylcyclopropenone alone.
 5 citations,
July 1988 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement”
5 citations,
July 1988 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” Diphencyprone therapy can effectively treat severe hair loss in motivated patients.
 1 citations,
February 2023 in “Deleted Journal”
1 citations,
February 2023 in “Deleted Journal” Diphenylcyclopropenone is effective for treating alopecia areata but has a high relapse rate.
 1 citations,
January 2015 in “Springer eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2015 in “Springer eBooks” The document says a skin condition called alopecia areata causes hair loss and stress, and is treated with strong skin creams, injections, or other therapies, but treatment success varies.
 January 2017 in “Nasza Dermatologia Online”
January 2017 in “Nasza Dermatologia Online” Both treatments helped hair regrowth in alopecia areata, with isopropanol being better tolerated.
 July 2021 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
July 2021 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Low testosterone levels may contribute to female pattern hair loss in men.
 2 citations,
May 2012 in “Indian drugs”
2 citations,
May 2012 in “Indian drugs” Finasteride, a hair loss treatment, works better and is more stable when delivered through specially prepared gels, leading to increased hair growth.
10 citations,
January 2012 in “Case reports in medicine” Diphencyprone can cause unexpected and possibly permanent vitiligo.

Stem cells can improve skin grafts by enhancing blood flow and hair growth.

The polyherbal hair mask is a safe and effective alternative for improving hair health.

MagicalRemedies serum effectively promotes healthy hair growth and reduces damage.

The new gel for hair loss is safe, effective, and reduces side effects.

The herbal shampoo effectively reduces dandruff and hair fall.

Curry leaves offer health benefits and can be used safely in various forms for digestion, diabetes control, and hair growth.
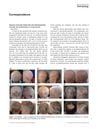 1 citations,
November 2019 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
November 2019 in “International Journal of Dermatology” A 6-year-old girl with alopecia universalis regrew most of her hair after treatment with simvastatin/ezetimibe, minoxidil, and prednisolone.
 13 citations,
June 2010 in “Journal of dermatological treatment”
13 citations,
June 2010 in “Journal of dermatological treatment” Diphencyprone is effective for treating patchy hair loss in alopecia areata, but tacrolimus is not.
 September 2022 in “Dermatology and therapy”
September 2022 in “Dermatology and therapy” Contact immunotherapy might help treat various skin conditions, but more research is needed to confirm its safety and effectiveness.
 January 2014 in “International Journal of Trichology”
January 2014 in “International Journal of Trichology” A man had an unusual type of hair loss that didn't match known patterns and didn't improve with treatment.
 321 citations,
March 2015 in “Nature”
321 citations,
March 2015 in “Nature” Super-enhancers controlled by pioneer factors like SOX9 are crucial for stem cell adaptability and identity.
 268 citations,
April 2009 in “International Journal of Pharmaceutics”
268 citations,
April 2009 in “International Journal of Pharmaceutics” Niosomes improve minoxidil skin delivery for hair loss treatment.
 260 citations,
January 2019 in “Pharmaceutics”
260 citations,
January 2019 in “Pharmaceutics” Niosomes are a promising, stable, and cost-effective drug delivery system with potential for improved targeting and safety.

























