 October 2023 in “The Cochrane library”
October 2023 in “The Cochrane library” The medicine baricitinib was found to notably improve hair regrowth in alopecia areata, but more research is needed on its side effects and other treatments.
7 citations,
June 2000 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Foam corticosteroid covers as well as traditional forms.
3 citations,
August 2019 in “PubMed” Topical corticosteroid foams are effective, safe, and easy to use for treating various skin conditions.
 January 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
January 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” The document concludes that alopecia has various forms, each with specific treatments, but no definitive cure for certain types like CCCA has been proven.
21 citations,
January 2007 in “Journal of Drugs in Dermatology” The laser effectively removes hair for skin types IV and V but is less effective for type VI.
227 citations,
April 2020 in “Cell” More precise, personalized therapies are needed for autoimmune diseases.
 January 2004 in “Side effects of drugs annual”
January 2004 in “Side effects of drugs annual” Certain skin drugs and topical agents, including some natural extracts and fragrances, can cause allergic reactions. Some hair dyes and extensions, as well as minoxidil, a hair growth treatment, can also cause allergies. Botulinum toxin A can effectively reduce sweat but may have temporary side effects.
April 2024 in “Cosmetics” Microneedling improves skin and hair conditions by enhancing treatment absorption and stimulating growth factors.
January 2023 in “Indian journal of pharmacy practice” Over-the-counter cosmetic creams can cause skin damage on the face that is visible under dermoscopy and confirmed by tissue analysis.

Topical corticosteroid treatment showed no significant difference from placebo in treating alopecia areata in children.
 6 citations,
February 2003 in “Anais brasileiros de dermatologia/Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia”
6 citations,
February 2003 in “Anais brasileiros de dermatologia/Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” Topical corticosteroid was not more effective than placebo for children's alopecia areata, and atopy did not change treatment results.
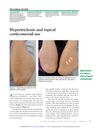 February 2022 in “Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine”
February 2022 in “Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine” Prolonged use of topical corticosteroids can cause excessive hair growth.
 August 1994 in “Drugs & Therapy Perspectives”
August 1994 in “Drugs & Therapy Perspectives” Psoriasis treatments range from topical creams to systemic medications with serious side effects, and while treatments can manage symptoms, there is no cure.
38 citations,
November 2006 in “Pediatric dermatology” Infants with scalp injuries developed a skin condition that improved with steroid creams.
 June 2022 in “Journal of pharmaceutical research international”
June 2022 in “Journal of pharmaceutical research international” Alopecia causes patchy hair loss and can be diagnosed with new techniques; treatments like strong creams and contact immunotherapy can help.
 25 citations,
July 2021 in “Journal of Medical Virology”
25 citations,
July 2021 in “Journal of Medical Virology” COVID-19 can cause various skin issues, including rashes and hair loss, which usually heal on their own and don't always indicate severe illness.
 5 citations,
February 2014 in “PubMed”
5 citations,
February 2014 in “PubMed” Hair loss in Telogen effluvium is often chronic, linked to stress, and lacks a confirmed treatment, but topical corticosteroids may be used.
 April 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Long-term Imiquimod treatment causes initial skin inflammation that lessens over time, and topical corticosteroids reduce this inflammation and cytokines in a mouse model of psoriasis.
A 21-year-old with lichen planopilaris was successfully treated, stopping disease progression and preventing crusts.

The document concludes that various skin conditions have specific treatments and that adequate calcium intake may prevent osteoporosis.

Melanocyte transplantation can safely restore skin color, especially in stable vitiligo, but must be chosen carefully based on the disease phase.
July 1974 in “Archives of dermatology” The woman's widespread skin condition did not improve despite various treatments.
113 citations,
May 2007 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” The study found that steroids and tetracycline helped treat active Lichen planopilaris, and hair transplants were good for later stages.
12 citations,
October 2013 in “British Journal of Dermatology” The meeting concluded with optimism about increasing research and better management of vitiligo.
9 citations,
September 2020 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology” A woman developed vitiligo from repeated eyebrow microblading.
 January 2024 in “JAAD case reports”
January 2024 in “JAAD case reports” Netherton syndrome can cause severe and chronic vulvovaginal symptoms that may improve with continuous oral contraceptives.

COVID-19 can cause skin problems and affect dermatology treatments, with recommendations for skin care and cautious use of certain drugs.
July 2019 in “Indian dermatology online journal” Alopecia areata can show unusual red-dotted vessels and dithranol treatment may mask typical patterns.
 6 citations,
July 2015 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
6 citations,
July 2015 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” A man developed an allergic skin reaction after using brimonidine for rosacea.
6 citations,
October 2006 Understanding repigmentation mechanisms in vitiligo can improve treatments and patient outcomes.
















