 27 citations,
April 2011 in “International journal of legal medicine”
27 citations,
April 2011 in “International journal of legal medicine” In situ DNA labeling in hair can help predict forensic DNA analysis success.
 22 citations,
April 2018 in “Pharmaceutics”
22 citations,
April 2018 in “Pharmaceutics” New methods improve how well skin treatments work by helping drugs get through the skin barrier.
 19 citations,
January 2021 in “Experimental dermatology”
19 citations,
January 2021 in “Experimental dermatology” Acne inversa is an epithelial-driven disease where inflammation is caused by cyst rupture, and treatments should focus on preventing tendril growth for better results.
 19 citations,
July 2009 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
19 citations,
July 2009 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” The study found that long-term sun exposure does not significantly affect follicular plugs on the scalp, and the scalp's appearance is unique compared to other body parts.
 17 citations,
December 2003 in “Veterinary dermatology”
17 citations,
December 2003 in “Veterinary dermatology” Some masked palm civets in Japan have a skin disease caused by mites.
 16 citations,
September 2018 in “Scientific reports”
16 citations,
September 2018 in “Scientific reports” Scientists created keratinocyte cell lines from human hair that can differentiate similarly to normal skin cells, offering a new way to study skin biology and diseases.
 16 citations,
August 1992 in “Archives of dermatological research”
16 citations,
August 1992 in “Archives of dermatological research” Lab-grown nail cells show characteristics similar to natural nail and hair.
 15 citations,
July 2004 in “Journal of morphology”
15 citations,
July 2004 in “Journal of morphology” Monotreme hair structure and protein distribution are similar to other mammals, but their inner root sheath cornifies differently, suggesting a unique evolution from reptile skin.
 13 citations,
January 2021 in “Scientific Reports”
13 citations,
January 2021 in “Scientific Reports” Pannexin 3 helps skin and hair growth by controlling a protein called Epiprofin.
 12 citations,
August 2017 in “Archives of Pharmacal Research”
12 citations,
August 2017 in “Archives of Pharmacal Research” Lecithin-based microparticles can deliver minoxidil for hair growth effectively with less skin irritation.
 10 citations,
October 1993 in “Archives of dermatological research”
10 citations,
October 1993 in “Archives of dermatological research” Vitamin D compounds may help treat psoriasis by promoting skin cell differentiation.
 8 citations,
May 1998 in “Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery”
8 citations,
May 1998 in “Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery” Acne is caused by increased sebum, abnormal skin shedding, bacteria, and inflammation, not dirt; treatments vary from creams to antibiotics or isotretinoin, with severe cases needing a dermatologist's care.
 5 citations,
December 2020 in “Experimental dermatology”
5 citations,
December 2020 in “Experimental dermatology” A specific type of skin cell creates an opening for hair to grow out, and problems with this process can lead to skin conditions.
 4 citations,
January 2018 in “Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology”
4 citations,
January 2018 in “Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology” The document concludes that hair follicles have a complex environment and our understanding of it is growing, but there are limitations when applying animal study findings to humans.
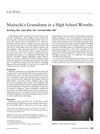 2 citations,
October 2019 in “Current sports medicine reports”
2 citations,
October 2019 in “Current sports medicine reports” A high school wrestler's skin rash was cured with antifungal medication after a misdiagnosis and incorrect treatment led to a fungal infection.
 2 citations,
March 2018 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
2 citations,
March 2018 in “The Journal of Dermatology” The "color-transition sign" helps tell apart alopecia areata incognita from telogen effluvium by looking at hair color changes.
 1 citations,
January 2009 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2009 in “Elsevier eBooks” The document concludes that a deeper understanding of skin aging and photodamage is needed to create better skin treatments.
 April 2024 in “Cell death and differentiation”
April 2024 in “Cell death and differentiation” Cell death shapes skin stem cell environments, affecting inflammation, repair, and cancer.
 December 2022 in “Journal of medical sciences and health”
December 2022 in “Journal of medical sciences and health” Examining nail biopsies is useful for diagnosing nail diseases.
 March 2022 in “Journal of South Asian Association of Pediatric Dentistry”
March 2022 in “Journal of South Asian Association of Pediatric Dentistry” Dentists should start preventive treatments early for children with Ichthyosis Vulgaris to avoid dental problems.
 November 2021 in “Journal of pharmaceutical research international”
November 2021 in “Journal of pharmaceutical research international” Herbal depilatories are safer and cause fewer side effects than chemical ones for hair removal.
 January 2019 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2019 in “Springer eBooks” Some chemicals and drugs can cause hair loss, which usually grows back after stopping the treatment.

Cornification is the process where living skin cells die to create a protective barrier, and problems with it can cause skin diseases.

The chapter explains that there are many genetic skin disorders affecting skin cell formation, including both common and rare types.
 August 2014 in “Springer eBooks”
August 2014 in “Springer eBooks” Certain gene mutations can weaken the skin barrier and, when combined with environmental factors, lead to eczema and severe itching.
 January 2012 in “The Japanese Journal of Veterinary Dermatology”
January 2012 in “The Japanese Journal of Veterinary Dermatology” The dog's hair loss healed on its own without treatment.
 438 citations,
October 2010 in “Oncogene”
438 citations,
October 2010 in “Oncogene” Keratins help protect cells, aid in cancer diagnosis, and influence cancer behavior and treatment.
 293 citations,
November 2011 in “Nature”
293 citations,
November 2011 in “Nature” The circadian clock affects skin stem cell behavior, impacting aging and cancer risk.
 277 citations,
July 2011 in “Journal of the Dermatology Nurses’ Association”
277 citations,
July 2011 in “Journal of the Dermatology Nurses’ Association” The skin's layers protect, sense, and regulate the body's internal balance, but can be prone to cancer.
 263 citations,
February 2013 in “Wiley interdisciplinary reviews. Nanomedicine and nanobiotechnology”
263 citations,
February 2013 in “Wiley interdisciplinary reviews. Nanomedicine and nanobiotechnology” Polymeric nanoparticles show promise for treating skin diseases.






























