 19 citations,
March 1988 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
19 citations,
March 1988 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Hair shaft dysplasias are abnormal hair conditions that can be inherited or acquired and may signal other health issues, with limited treatment options available.
 42 citations,
October 2009 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
42 citations,
October 2009 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Mutations in the KRT85 gene cause hair and nail problems.
[object Object] 14 citations,
June 1989 in “Journal of dermatology” Three siblings had both Vohwinkel's disease and congenital alopecia, with no effective treatment.
12 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian dermatology online journal” The document reports a unique case of woolly hair with a combination of conditions not previously seen together.
7 citations,
January 2012 in “International journal of trichology” Permanent hair removal with lasers may cure itchy black hair bristles on the back.
 6 citations,
May 1993 in “Archives of Disease in Childhood”
6 citations,
May 1993 in “Archives of Disease in Childhood” Children's hair loss can be caused by many factors, including autoimmune diseases, emotional stress, genetics, and infections, with treatment and prognosis varying.
 2 citations,
December 2004 in “Medicine”
2 citations,
December 2004 in “Medicine” Different hair and scalp disorders cause hair loss or excess hair growth, with various treatments available depending on the specific condition.
 1 citations,
October 2014 in “Paediatrics and Child Health”
1 citations,
October 2014 in “Paediatrics and Child Health” The document concludes that proper diagnosis and management of hair loss in children require a detailed examination and understanding of various hair disorders.
 June 2021 in “International journal of research in dermatology”
June 2021 in “International journal of research in dermatology” Shaving and avoiding brushing improved the patient's beard hair condition.
 April 2020 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society”
April 2020 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society” A patient with untreated congenital adrenal hyperplasia had large benign tumors in her adrenal glands removed, improving her symptoms.
 2 citations,
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
2 citations,
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” Trichoscopy is a useful tool for diagnosing and managing hair and scalp conditions, often better than traditional methods.
November 2021 in “CRC Press eBooks” Hair color is determined by melanin and can be affected by genetic conditions like albinism.

Minoxidil is better for female hair loss without hormonal issues, cyproterone acetate for those with; people with treated congenital heart disease have lower life quality; personality differs in types of infertility; oral terbinafine is best for toenail fungus; bladder training reduces incontinence; nurse clinics help with heart disease; weight loss improves body composition and liver disease; computer training cuts drug errors.
 36 citations,
June 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
36 citations,
June 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Dermoscopy is useful for diagnosing various skin, hair, and nail disorders and can reduce the need for biopsies.
 11 citations,
August 2019 in “The Journal of Sexual Medicine”
11 citations,
August 2019 in “The Journal of Sexual Medicine” Women with nonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia experience more sexual dysfunction and distress.
 3 citations,
April 2012 in “Bioinformation”
3 citations,
April 2012 in “Bioinformation” Two specific SNPs in the TRPS1 gene cause excessive hair growth by altering the protein's structure.
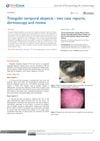 2 citations,
February 2018 in “Journal of dermatology & cosmetology”
2 citations,
February 2018 in “Journal of dermatology & cosmetology” Triangular temporal alopecia is a benign hair loss pattern best diagnosed with dermoscopy, with limited treatment options like surgery and hair transplantation.
July 2023 in “International journal of physiology” Hypertrichosis lanuginosa causes excessive fine hair growth, often linked to genetics or cancer, with limited treatment options.
January 2023 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal” A 23-year-old man has a benign, non-progressive hair loss patch that doesn't respond to treatment but can be cosmetically treated.
January 2022 in “The Pan African medical journal” Hypertrichosis causes excessive hair growth and needs psychological support due to its impact on self-esteem.
[object Object] The chapter explains causes of hair loss and excessive hair growth in animals.
 April 2020 in “International journal of research in dermatology”
April 2020 in “International journal of research in dermatology” An 8-year-old girl has a rare, irreversible hair loss condition caused by a genetic mutation.
 September 2010 in “Companion Animal”
September 2010 in “Companion Animal” The guide explains how to diagnose and treat hair loss in dogs, covering causes and treatments, with some conditions lacking treatment options.
 August 2010 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
August 2010 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” New hair regrowth model introduced, imiquimod kills skin cancer cells, T-cadherin loss makes skin cancer more invasive, no strong link between PTCH1 gene and skin cancer after transplant, and male teens more likely to have hereditary hair loss.
 July 2010 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
July 2010 in “British Journal of Dermatology” New hair regrowth model proposed, imiquimod found to kill skin cancer cells, T-cadherin loss linked to invasive skin cancer, no clear gene link to skin cancer after transplant, and study on children's hair loss shows male dominance and genetic ties.
125 citations,
February 2003 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” The document explains the types of excessive hair growth and how to manage it.
 67 citations,
September 2008 in “Dermatologic therapy”
67 citations,
September 2008 in “Dermatologic therapy” Hirsutism is excessive hair growth in women often caused by polycystic ovarian syndrome, and identifying the cause is important for managing associated health risks.
16 citations,
January 2010 in “Journal of Korean medical science/Journal of Korean Medical Science” A Korean boy's skin and digestive symptoms were caused by a rare genetic disorder that affects zinc absorption, and he got better with zinc supplements.
13 citations,
June 2006 in “Fertility and Sterility” Nonclassic 21-hydroxylase deficiency is a common, treatable genetic disorder causing reversible symptoms like acne and hair loss.
 10 citations,
December 1995 in “Journal of women's health”
10 citations,
December 1995 in “Journal of women's health” Finasteride reduces hair growth in women with hirsutism and works better with electrolysis.



















