 June 1999 in “Proceedings of SPIE”
June 1999 in “Proceedings of SPIE” The CO₂ laser is better for hair transplantation because it causes less damage than the Ho:YAG laser.
 27 citations,
August 2014 in “Journal of Cosmetic and Laser Therapy”
27 citations,
August 2014 in “Journal of Cosmetic and Laser Therapy” Different lasers and radiofrequency affect skin differently, important for dermatologists to choose the right treatment.
 25 citations,
August 2017 in “Lasers in Medical Science”
25 citations,
August 2017 in “Lasers in Medical Science” Fractional lasers seem effective and safe for treating hair loss, but more research is needed to find the best treatment methods.
[object Object]  18 citations,
August 2018 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America”
18 citations,
August 2018 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America” Lasers, microneedling, and PRP improve skin rejuvenation and repair, with PRP enhancing the effects when combined with other treatments.
 15 citations,
January 1996 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine”
15 citations,
January 1996 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine” Lasers in hair transplantation may have potential but require caution due to possible damage and reduced graft survival.
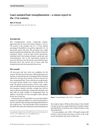 11 citations,
June 2005 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
11 citations,
June 2005 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Lasers in hair transplantation show promise but are not yet standard, with current methods causing some side effects and needles still being preferred for creating recipient sites.
 April 2003 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
April 2003 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Lasers are effective for some skin conditions but can cause side effects like scarring and pigment changes; careful selection is important, and botulinum toxin type A is successful in reducing sweat in palmar hyperhidrosis.
 19 citations,
August 2007 in “Seminars in Plastic Surgery”
19 citations,
August 2007 in “Seminars in Plastic Surgery” Newer skin resurfacing lasers reduce damage and scarring, with some approved for safe use and minimal side effects.
 January 2023 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine ”
January 2023 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine ” Fractional CO2 laser treatment could be effective for alopecia areata.
 10 citations,
July 1997 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
10 citations,
July 1997 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Laser hair transplantation can be effective but should be limited to small areas and requires more training to ensure safety and effectiveness.
 3 citations,
August 2002 in “Current Opinion in Otolaryngology & Head and Neck Surgery”
3 citations,
August 2002 in “Current Opinion in Otolaryngology & Head and Neck Surgery” Hair transplantation, especially follicular unit micrografting, was the top treatment for male pattern baldness, with a focus on natural results and ongoing improvements in both surgical and medical management.
 June 2002 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
June 2002 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Hair transplantation has improved to more natural-looking results and is complemented by effective non-surgical treatments, with ongoing research into hair follicle cloning.
 January 2001 in “Current problems in dermatology”
January 2001 in “Current problems in dermatology” Hair transplantation has improved to use smaller grafts for a natural look and may include follicle cloning in the future; non-surgical treatments are also effective.
 June 1997 in “The American Journal of Cosmetic Surgery”
June 1997 in “The American Journal of Cosmetic Surgery” Gradual improvements in hair restoration techniques are safer and more effective than drastic changes.
 January 2024 in “RSC pharmaceutics”
January 2024 in “RSC pharmaceutics” Removing the outer skin layer increases drug absorption and offers non-invasive treatment options, with some methods allowing for quick skin recovery.
 17 citations,
January 2021 in “Dermatology and Therapy”
17 citations,
January 2021 in “Dermatology and Therapy” Laser-assisted drug delivery has shown improved treatment outcomes for skin conditions and has potential to reduce side effects and treatment time.
 December 2024 in “Anti-Aging Eastern Europe”
December 2024 in “Anti-Aging Eastern Europe” PRP is effective for skin rejuvenation, hair restoration, and acne scar treatment.
1 citations,
September 2021 in “Rossijskij žurnal kožnyh i veneričeskih boleznej” Osteoma cutis is a rare, benign skin condition where bone forms in the skin.
 September 2024 in “Pakistan Journal of Science”
September 2024 in “Pakistan Journal of Science” Laser treatments, especially low-level laser therapy, can improve hair growth, but more research is needed.
 July 1998 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
July 1998 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Various techniques and tools for hair restoration were presented in 1998, including a mathematical model for donor area, use of lasers in surgery, methods for controlling grafted hair direction, and ways to increase graft yield. Satisfaction rates were around 39%, and studies showed trauma and dehydration can damage hair follicles.
 1 citations,
April 1998 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
1 citations,
April 1998 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Surgical skin treatments improved with new methods like laser resurfacing, combined techniques, and better hair and fat removal options.
 26 citations,
May 2017 in “Lasers in Medical Science”
26 citations,
May 2017 in “Lasers in Medical Science” Laser therapy and hair growth factors significantly improve hair density in male baldness.
 January 2025 in “Lasers in Medical Science”
January 2025 in “Lasers in Medical Science” Combining fractional CO2 laser with topical dutasteride is more effective for treating male hair loss than using the laser alone.
 3 citations,
August 1995 in “Journal of Clinical Laser Medicine & Surgery”
3 citations,
August 1995 in “Journal of Clinical Laser Medicine & Surgery” Using a CO₂ laser for hair transplants improves the surgery and may become important in future hair restoration.
[object Object]  5 citations,
May 1999 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
5 citations,
May 1999 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Lasers can effectively treat pseudofolliculitis barbae, but insurance often doesn't cover it, possibly due to racial bias.
 1 citations,
April 2022 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine ”
1 citations,
April 2022 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine ” Fractional laser therapy may help regrow hair in alopecia areata.
 January 2018 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2018 in “Springer eBooks” Lasers are less favored for hair transplant surgery but show promise for hair growth in controlled trials.
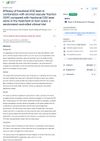 April 2023 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
April 2023 in “Research Square (Research Square)” Combining stromal vascular fraction (SVF) injections with fractional CO2 laser treatment is more effective for treating burn scars than using the laser alone.
 January 1998 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine”
January 1998 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine” Lasers are effective and safe for various medical treatments, including cancer, wound healing, and skin conditions.
27 citations,
July 2013 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Lasers have become precise tools in skin treatment and diagnosis, with ongoing advancements improving their effectiveness.




























