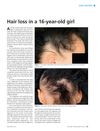
 November 2014 in “Prescriber”
November 2014 in “Prescriber” The 16-year-old girl with hair loss was successfully treated for alopecia areata, leading to significant hair regrowth.
 38 citations,
December 2011 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia”
38 citations,
December 2011 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” Skin diseases significantly lower the quality of life for patients in southern Brazil, especially for younger, single, and lower-income individuals.
 10 citations,
October 2019 in “Acta Pharmaceutica”
10 citations,
October 2019 in “Acta Pharmaceutica” Medicinal plants are used to treat skin conditions, but more evidence is needed before recommending them widely.
 2 citations,
January 2019
2 citations,
January 2019 The document concludes that autoimmune skin disorders are treated with corticosteroids and immunosuppressive drugs.
 September 2014 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
September 2014 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Diabetes can cause a variety of skin disorders, some of which may signal more serious health issues.
 July 2018 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
July 2018 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Mindfulness reduces anxiety and depression in skin disease patients; dermatologists and psychiatrists often lack confidence in treating psychodermatological conditions.
64 citations,
January 2009 in “Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology” Interferon and ribavirin can cause serious skin reactions and other health issues.
 August 2024 in “Indian Journal of Skin Allergy”
August 2024 in “Indian Journal of Skin Allergy” Stem-cell therapy shows promise for skin conditions but needs more research.
 March 2014 in “Pediatric Clinics of North America”
March 2014 in “Pediatric Clinics of North America” The document discusses how to identify and manage common skin conditions in children.
 67 citations,
July 2016 in “Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders”
67 citations,
July 2016 in “Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders” Stress can worsen skin conditions by affecting hormone levels and immune response.
 12 citations,
October 1995 in “The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism”
12 citations,
October 1995 in “The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism” Skin changes can indicate hormonal imbalances and help diagnose endocrine disorders.
 8 citations,
September 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
8 citations,
September 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Some diets and supplements might help with skin disorders, but their effectiveness varies and more research is needed.
 2 citations,
June 2021 in “Cosmoderma”
2 citations,
June 2021 in “Cosmoderma” Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) shows promise in skin and hair treatments but results vary with preparation methods.

PRP therapy effectively treats hair loss, wrinkles, scars, ulcers, and skin pigmentation disorders.
 4 citations,
March 2009 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
4 citations,
March 2009 in “British Journal of Dermatology” The conference highlighted new dermatological treatments and emphasized early intervention and addressing conditions lacking evidence-based treatments.
 24 citations,
September 2008 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology”
24 citations,
September 2008 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology” Repigmentation in vitiligo may come from melanocyte stem cells in the skin.

Treating vitiligo with stem cells and melanocytes from hair, along with UVB light, works better than without the light.
 63 citations,
December 2002 in “Archives of Dermatology”
63 citations,
December 2002 in “Archives of Dermatology” The 308-nm excimer laser is a promising treatment for vitiligo with varying success and mild side effects.
 18 citations,
November 2018 in “Annals of the Academy of Medicine Singapore”
18 citations,
November 2018 in “Annals of the Academy of Medicine Singapore” Sulfasalazine can cause severe allergic reactions leading to long-term autoimmune issues like hair loss and skin discoloration.
 17 citations,
December 2011 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
17 citations,
December 2011 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” People with vitiligo may have a lower risk of heart disease.

A teenager had both alopecia areata and vitiligo, which are rare to occur together.
 74 citations,
May 2016 in “Current opinion in pediatrics, with evaluated MEDLINE/Current opinion in pediatrics”
74 citations,
May 2016 in “Current opinion in pediatrics, with evaluated MEDLINE/Current opinion in pediatrics” Both vitiligo and alopecia areata involve an immune response triggered by stress and specific genes, with treatments targeting this pathway showing potential.
 59 citations,
June 2022 in “Frontiers in medicine”
59 citations,
June 2022 in “Frontiers in medicine” There are still challenges in diagnosing and treating chronic skin diseases, but there is hope for future improvements.
 56 citations,
March 2016 in “International Wound Journal”
56 citations,
March 2016 in “International Wound Journal” Skin grafts are effective for chronic leg ulcers, especially autologous split-thickness grafts for venous ulcers, but more data is needed for diabetic ulcers.
 45 citations,
January 1999 in “Dermatology”
45 citations,
January 1999 in “Dermatology” The VQ-Dermato is a reliable French questionnaire for measuring quality of life in chronic skin disorder patients.
 41 citations,
August 2007 in “European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology”
41 citations,
August 2007 in “European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology” A woman's total hair loss from hepatitis C treatment grew back after stopping the medication.
 34 citations,
April 2008 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
34 citations,
April 2008 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Skin problems like itching, dry skin, and hair loss are more common in hepatitis C patients after interferon treatment, but lichen planus is not linked to the infection.
 27 citations,
March 2018 in “Allergy and asthma proceedings”
27 citations,
March 2018 in “Allergy and asthma proceedings” People with alopecia areata often have higher rates of allergies and autoimmune diseases.
 9 citations,
May 2013 in “JAMA Dermatology”
9 citations,
May 2013 in “JAMA Dermatology” A woman's hair turned white after taking a cancer drug called dasatinib.
 9 citations,
November 2012 in “Hepatology Research”
9 citations,
November 2012 in “Hepatology Research” A man lost all his hair permanently after hepatitis C treatment, a side effect not seen before.





























