 July 2022 in “International journal of dermatology, venereology and leprosy sciences”
July 2022 in “International journal of dermatology, venereology and leprosy sciences” More frequent and severe skin problems are linked to higher daily alcohol consumption.

Dupilumab helped improve skin and prevent new lesions in a child with a rare immune disorder and severe eczema.
 26 citations,
January 2017 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
26 citations,
January 2017 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Antidepressants might help with skin inflammation and improve conditions like psoriasis and eczema.
 September 2017 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
September 2017 in “Pediatric Dermatology” The document concludes that an experimental drug may help wound healing in Epidermolysis Bullosa, links Hydroa vacciniforme to EBV, discusses diagnosing hair loss disorders, finds many children with eczema have allergies, reviews the safety of a skin medication in children, notes side effects of a Duchenne's treatment, and identifies a marker for pediatric mastocytosis.
 1 citations,
April 2021 in “Nepal journal of dermatology, venereology & leprology”
1 citations,
April 2021 in “Nepal journal of dermatology, venereology & leprology” Skin diseases are changing, with more allergic and immune-related conditions, but infections remain a major concern.
 May 2023 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
May 2023 in “British Journal of Dermatology” COVID-19 can cause long-term skin problems and has changed how skin doctors work.
 May 2022 in “Journal of Education, Health and Sport”
May 2022 in “Journal of Education, Health and Sport” Skin diseases like psoriasis, lupus, and others can increase heart disease risk due to factors like chronic inflammation and genetic susceptibility.
Neutrophils are key in causing chronic itch in atopic dermatitis, and blocking CXCR3 could reduce this itch.
 January 2017 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
January 2017 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” The congress showed that psychological therapy can help skin condition patients, social media affects acne stigma, education improves atopic dermatitis, and patient satisfaction in dermatology is high, especially with good doctor engagement.
 January 2024 in “Frontiers in immunology”
January 2024 in “Frontiers in immunology” Histone modification is key in treating chronic inflammatory skin diseases.
64 citations,
January 2009 in “Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology” Interferon and ribavirin can cause serious skin reactions and other health issues.
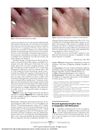 9 citations,
May 2013 in “JAMA Dermatology”
9 citations,
May 2013 in “JAMA Dermatology” Sunlight exposure improved a patient's skin condition, and there may be a link between a certain disease and skin growths; a leukemia treatment caused changes in hair color and growth.
6 citations,
October 1998 in “PubMed” Antifungal treatment can improve severe skin infections with cutaneous horns.
 14 citations,
April 2014 in “Medical Clinics of North America”
14 citations,
April 2014 in “Medical Clinics of North America” The document concludes that quick referral and appropriate treatments are crucial for managing common skin conditions and preventing permanent damage.
 October 2023 in “Journal of Medicine, University of Santo Tomas (JMUST Online)”
October 2023 in “Journal of Medicine, University of Santo Tomas (JMUST Online)” Elderly patients frequently suffer from skin conditions, especially inflammatory ones, highlighting the need for better healthcare.
31 citations,
July 2021 in “ImmunoTargets and therapy” Alopecia areata is an incurable autoimmune condition causing hair loss, with research aiming for better treatments.
28 citations,
June 2021 in “Frontiers in immunology” A protein called lfTSLP is important in causing allergic and other skin diseases and could be a target for treatment.
 8 citations,
February 2022 in “Vascular Health and Risk Management”
8 citations,
February 2022 in “Vascular Health and Risk Management” Some skin conditions may increase the risk of heart disease, and understanding their connection could lead to better treatments.
 2 citations,
September 2022 in “Cytotherapy”
2 citations,
September 2022 in “Cytotherapy” Fat-derived stem cells show promise for treating skin issues and improving wound healing, but more research is needed to confirm the best way to use them.
 2 citations,
September 2021
2 citations,
September 2021 The COVID-19 pandemic increased the use of teledermatology to treat skin conditions in low-income areas, despite challenges like poor photo quality.
 2 citations,
May 2020 in “Anais brasileiros de dermatologia/Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia”
2 citations,
May 2020 in “Anais brasileiros de dermatologia/Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” Primary health care in Florianópolis mostly treated simple skin conditions, while secondary care handled more complex skin diseases.
2 citations,
October 1974 in “Archives of Dermatology” The woman's skin condition persisted for 20 years despite treatments.
 August 2024 in “Indian Journal of Skin Allergy”
August 2024 in “Indian Journal of Skin Allergy” Stem-cell therapy shows promise for skin conditions but needs more research.
 115 citations,
November 2015 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology”
115 citations,
November 2015 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology” Children with atopic dermatitis often have sleep problems, affecting their growth and behavior.
 15 citations,
September 2018 in “Dermatologic therapy”
15 citations,
September 2018 in “Dermatologic therapy” Both emollients effectively reduced itching and improved skin moisture in xerotic eczema.
 September 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
September 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Abrocitinib at 100 mg and 200 mg daily may significantly improve moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis in patients 12 years and older.
 59 citations,
June 2022 in “Frontiers in medicine”
59 citations,
June 2022 in “Frontiers in medicine” There are still challenges in diagnosing and treating chronic skin diseases, but there is hope for future improvements.
 41 citations,
August 2007 in “European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology”
41 citations,
August 2007 in “European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology” A woman's total hair loss from hepatitis C treatment grew back after stopping the medication.
 34 citations,
April 2008 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
34 citations,
April 2008 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Skin problems like itching, dry skin, and hair loss are more common in hepatitis C patients after interferon treatment, but lichen planus is not linked to the infection.
 27 citations,
March 2018 in “Allergy and asthma proceedings”
27 citations,
March 2018 in “Allergy and asthma proceedings” People with alopecia areata often have higher rates of allergies and autoimmune diseases.
























