 January 2021 in “Benha Journal of Applied Sciences”
January 2021 in “Benha Journal of Applied Sciences” Prolactin levels and gene polymorphism are not linked to vitiligo severity but are related to BMI.
 November 2020 in “International journal of contemporary pediatrics”
November 2020 in “International journal of contemporary pediatrics” Two siblings had a rare immune disorder caused by a FOXN1 gene mutation.
 January 2020 in “Medical journal of clinical trials & case studies”
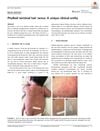
January 2020 in “Medical journal of clinical trials & case studies” A 37-year-old male with severe skin and internal issues has a rare inherited skin condition called dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa.
[object Object]  November 2018 in “Atlas of genetics and cytogenetics in oncology and haematology”
November 2018 in “Atlas of genetics and cytogenetics in oncology and haematology” WNT10B is linked to cancer development and affects survival and disease progression in various cancers.
 August 2018 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
August 2018 in “Pediatric Dermatology” A baby had a unique skin condition with a pale patch and surrounding dark hairs, not linked to other health issues.
 July 2018 in “Benha Journal of Applied Sciences”
July 2018 in “Benha Journal of Applied Sciences” Higher levels of miR-203 may contribute to hair loss in alopecia areata.
 April 2018 in “Nasza Dermatologia Online”
April 2018 in “Nasza Dermatologia Online” People with Down's syndrome are more likely to have syringomas.
 March 2018 in “Suez Canal University Medical Journal”
March 2018 in “Suez Canal University Medical Journal” NKG2D gene polymorphism doesn't affect SLE risk but may influence symptoms like rash and hair loss.

Different scalp and hair disorders are more common in certain ethnic groups, with the most common being androgenetic alopecia, which is treated with medications like minoxidil and finasteride.
 December 2016 in “Springer eBooks”
December 2016 in “Springer eBooks” A 45-year-old woman with autoimmune diseases experienced patchy hair loss due to alopecia areata, which has no cure but can be treated, with varying success.
 September 2016 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
September 2016 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” A gene mutation worsens skin irritation in mice due to a lack of certain fats.
 July 2015 in “Cambridge University Press eBooks”
July 2015 in “Cambridge University Press eBooks” Androgens like testosterone affect skin health and can lead to conditions such as acne and hair loss, with various treatments available.
 May 2015 in “Endocrinología y nutrición”
May 2015 in “Endocrinología y nutrición” The conclusion is that adult males with muscle weakness and hormonal imbalances should be tested for Kennedy's disease.
 January 2013 in “International Journal of Trichology”
January 2013 in “International Journal of Trichology” A new mutation in the TRPS1 gene was found in a Ukrainian girl with Trichorhinophalangeal syndrome type I.
 August 2012 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
August 2012 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Men with early hair loss may have a higher risk of enlarged prostate and possibly prostate cancer due to shared hormonal factors.
April 2012 in “Journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences” No effective treatment exists to stimulate hair growth in atrichia with papular lesions.
 January 2012 in “Else Kröner-Fresenius Symposia”
January 2012 in “Else Kröner-Fresenius Symposia” Maintaining DNA integrity in stem cells is crucial to prevent aging and cancer.
 January 2012 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
January 2012 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Some Greek melanoma patients have gene mutations linked to increased cancer risk, a new color feature helps diagnose melanoma, the incidence of a skin condition in the Netherlands is rare, and a gene possibly affects male-pattern baldness.
 November 2009 in “Journal of Pediatric Nursing”
November 2009 in “Journal of Pediatric Nursing” Nonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a common genetic disorder that can cause a range of symptoms and requires personalized treatment.
 November 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
November 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” The 2004 hair research meeting presented new findings on hair cell differentiation, genetic factors in hair loss, hair pigmentation, and potential targeted therapies.
 April 1974 in “Pediatric Research”
April 1974 in “Pediatric Research” The Naked (N) trait in mice is linked to lower glycine and tyrosine in hair proteins.
 December 2020 in “Skin appendage disorders”
December 2020 in “Skin appendage disorders” Finasteride may effectively treat hair loss in Klinefelter Syndrome patients.
 May 2004 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
May 2004 in “Pediatric Dermatology” Atopic dermatitis may have genetic causes and can be treated with pharmacologic methods, glycerin creams, and controlling Staphylococcus aureus colonization.
 August 1993 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
August 1993 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Testosterone metabolism in balding scalp cells may not be the main cause of hair loss.
 1540 citations,
October 2008 in “Fertility and Sterility”
1540 citations,
October 2008 in “Fertility and Sterility” The report concludes that PCOS is mainly a condition of excess male hormones and its definition may change as new information is discovered.
 1533 citations,
October 2008 in “Endocrine reviews”
1533 citations,
October 2008 in “Endocrine reviews” Mice without the vitamin D receptor have bone issues and other health problems, suggesting vitamin D is important for preventing various diseases in humans.
 1514 citations,
December 2011 in “Fertility and sterility”
1514 citations,
December 2011 in “Fertility and sterility” Experts agree that PCOS affects women's health in complex ways, but more research is needed to understand and treat it effectively.
[object Object]  1308 citations,
March 1998 in “Journal of bone and mineral research”
1308 citations,
March 1998 in “Journal of bone and mineral research” The vitamin D receptor is crucial for bone health and affects various body systems, with mutations potentially leading to disease.
 1039 citations,
February 2009 in “Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology”
1039 citations,
February 2009 in “Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology” Skin stem cells are crucial for maintaining and repairing the skin and hair, using a complex mix of signals to do so.
 991 citations,
January 2011 in “Nature Reviews Endocrinology”
991 citations,
January 2011 in “Nature Reviews Endocrinology” The document concludes that PCOS is a complex disorder caused by both genetic and environmental factors, affecting women's health in various ways, and requires personalized treatment.





























