 2 citations,
May 2019 in “Advances in wound care”
2 citations,
May 2019 in “Advances in wound care” Blood-derived CD34+ cells speed up healing, reduce scarring, and regrow hair in skin wounds.
 30 citations,
July 2019 in “PloS one”
30 citations,
July 2019 in “PloS one” Patients with Alopecia areata have fewer specific immune cells that normally regulate the immune system, which may contribute to the condition.
 130 citations,
November 2017 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
130 citations,
November 2017 in “Frontiers in Immunology” The conclusion is that Treg-targeted therapies have potential, but more knowledge of Treg biology is needed for effective treatments, including for cancer.
 January 2025 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
January 2025 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Potential therapeutic targets for scarring hair loss are identified.
 5 citations,
January 2016 in “Journal of Molecular Histology”
5 citations,
January 2016 in “Journal of Molecular Histology” Both main and alternative Wnt signaling are important for regrowing rodent whisker follicles.
Finasteride reduces blood vessel formation in seminal vesicles.
 106 citations,
March 2014 in “BioEssays”
106 citations,
March 2014 in “BioEssays” We need more research to better understand human hair follicle stem cells for improved treatments for hair loss and skin cancer.
92 citations,
December 2005 in “The Journal of clinical investigation/The journal of clinical investigation” Human hair follicle stem cells can be isolated using specific markers for potential therapeutic use.
 November 2013 in “Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature”
November 2013 in “Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature” Injecting CD34+ cell-containing platelet-rich plasma can improve pattern hair loss more than placental extract treatment.
 26 citations,
February 2020 in “Frontiers in genetics”
26 citations,
February 2020 in “Frontiers in genetics” The CORT, FGF5, and CD36 genes are crucial for the cold weather adaptation of Yanbian cattle.
 March 2024 in “Journal of functional foods”
March 2024 in “Journal of functional foods” Collagen peptides from marine and bovine sources may help prevent hair loss by affecting hair follicle stem cells differently.
May 2022 in “The journal of immunology/The Journal of immunology” FOXN1 is crucial for thymus development and immune response in Xenopus laevis.
 May 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
May 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” LED light helps human hair root cells grow and move by activating certain cell pathways.
52 citations,
February 2012 in “PloS one” Lack of Ctip2 in skin cells delays wound healing and disrupts hair follicle stem cell markers in mice.
 56 citations,
May 2017 in “Nature Cell Biology”
56 citations,
May 2017 in “Nature Cell Biology” Hair can regrow after certain stem cells are lost because other stem cells can take over their role.
 6 citations,
February 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
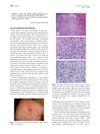
6 citations,
February 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” A woman had a rare skin condition with recurring painful nodules that heal in 6 weeks, often without needing treatment.
 December 2022 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
December 2022 in “Research Square (Research Square)” The QuantAnts machines can find cancer markers and create CRISPR targets for them.
 8 citations,
August 2016 in “Journal of pathology and translational medicine”
8 citations,
August 2016 in “Journal of pathology and translational medicine” CD99 is highly present in certain skin cells and could help treat skin conditions.
 September 2016 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
September 2016 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” The protein aPKCλ is crucial for keeping hair follicle stem cells inactive and for hair growth and regeneration.
 11 citations,
June 2021 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology”
11 citations,
June 2021 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology” Melatonin helps goat hair stem cells grow and maintain their ability to become different cell types.
4 citations,
January 2018 in “Microscopy research” Scientists found markers called CD34 and CD200 that help identify stem cells in mouse and human hair follicles.
20 citations,
December 2013 in “PTR. Phytotherapy research/Phytotherapy research” Ginsenoside Rg3 may help hair growth by increasing a growth-related protein in hair cells.
 9 citations,
April 2019 in “Molecules”
9 citations,
April 2019 in “Molecules” Blackcurrant extract may help reduce hair loss by promoting stem cell activity in hair follicles.
 January 2011 in “Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature”
January 2011 in “Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature” Bald men with male pattern baldness still have hair stem cells, but lack certain cells needed to grow hair.
 January 2011 in “Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature”
January 2011 in “Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature” Bald men with male pattern baldness still have hair stem cells, but lack certain cells needed for hair growth.
 August 2016 in “Journal of Dermatology”
August 2016 in “Journal of Dermatology” A chemical called 5-Bromo-2′-deoxyuridine caused rapid hair loss in mice by killing certain skin cells through a specific cell death pathway.
4 citations,
January 2017 in “Journal of veterinary medical science” A dog had a rare skin tumor called desmoplastic tricholemmoma.
 6 citations,
January 2017 in “Journal of toxicologic pathology”
6 citations,
January 2017 in “Journal of toxicologic pathology” Rabbit skin with active hair growth shows thicker, redder areas due to larger, more numerous hair follicles and increased blood vessels.
 4 citations,
August 2005 in “Archives of Dermatological Research”
4 citations,
August 2005 in “Archives of Dermatological Research” Higher p63 and CD34 levels found in specific scalp areas may affect hair loss progression.
 30 citations,
February 2017 in “Histochemistry and Cell Biology”
30 citations,
February 2017 in “Histochemistry and Cell Biology” TPA promotes hair growth by increasing stem cell activity and activating specific cell signals.























