 1 citations,
August 2017 in “Semiotica”
1 citations,
August 2017 in “Semiotica” The paper concludes that breast cancer treatment involves complex interactions between medical symptoms, patient experiences, and commercial influences, requiring a holistic approach.
 December 2024 in “Cureus”
December 2024 in “Cureus” Chemotherapy worsens nutritional status in breast cancer patients, requiring targeted nutritional strategies.
 January 2023 in “International journal of advances in scientific research and engineering”
January 2023 in “International journal of advances in scientific research and engineering” Anthocyanins from fruits and vegetables may help prevent and treat colorectal cancer safely.
[object Object]  2 citations,
January 2014 in “Springer eBooks”
2 citations,
January 2014 in “Springer eBooks” The book details skin conditions in older adults, their link to mental health, cancer treatment importance, hair loss remedies, and managing autoimmune and itchy skin.
 2 citations,
July 2009 in “Circulation Research”
2 citations,
July 2009 in “Circulation Research” CD133+ progenitor cells have therapeutic potential for diabetic ulcers and heart attack recovery, with manageable risks.
 1 citations,
August 2024 in “Polymers”
1 citations,
August 2024 in “Polymers” Bacterial cellulose is a promising material for biomedical uses but needs improvements in antimicrobial properties and degradation rate.
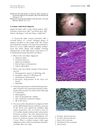 2 citations,
August 2010 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
2 citations,
August 2010 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” A 65-year-old woman has a growing bald spot on her scalp.
 July 2016 in “American Journal of Dermatopathology”
July 2016 in “American Journal of Dermatopathology” The meeting showcased rare skin disease cases, highlighting the need for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
 5 citations,
January 2001 in “Advances in protein chemistry”
5 citations,
January 2001 in “Advances in protein chemistry” 5α-reductase inhibitors help treat disorders caused by DHT and have potential for future therapies.
 4 citations,
January 2019 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
4 citations,
January 2019 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Scalp basal cell carcinoma may be more aggressive and harder to treat than other types, requiring special attention and further research.
 October 2023 in “Biomedical science and engineering”
October 2023 in “Biomedical science and engineering” Innovative methods are reducing animal testing and improving biomedical research.
56 citations,
July 2014 in “PloS one” SARMs may be an effective treatment for a certain type of breast cancer by blocking cancer growth and spread.
 34 citations,
July 2009 in “Journal of Cell Science”
34 citations,
July 2009 in “Journal of Cell Science” ΔNp63α helps control a protein that stops cancer cells from spreading.
 October 2024 in “Frontiers in Oncology”
October 2024 in “Frontiers in Oncology” Keratin 18 helps diagnose and predict cancer progression and affects cancer growth and spread.
 September 2006 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
September 2006 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Some aggressive scalp cancers are hard to treat and can be deadly, even when removed with specialized surgery.
 88 citations,
July 2014 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
88 citations,
July 2014 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Targeted cancer therapies often cause skin reactions, so dermatologists must manage these effects.
 19 citations,
October 2008 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
19 citations,
October 2008 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Anti-cancer treatments can cause reversible hair loss, skin sensitivity, pigmentation changes, nail damage, and skin reactions, with a need for more research on managing these side effects.
 12 citations,
March 2016 in “Life Sciences”
12 citations,
March 2016 in “Life Sciences” The new chemotherapy combination of WP 631 and Epothilone B shows enhanced effectiveness against ovarian cancer but requires more research on its safety.
 September 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
September 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Non-white organ transplant patients have worse skin cancer outcomes due to later diagnosis and treatment.

Google should ban ads targeting cancer patients with sensitive health-related keywords to protect them from misleading information.
 September 2023 in “Curēus”
September 2023 in “Curēus” Reproductive hormones play a crucial role in breast cancer development and treatment challenges.
1 citations,
March 2021 in “F1000Research” Plant-based compounds might be effective, low-side-effect treatments for prostate cancer by blocking a specific enzyme.
 May 2011 in “Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism”
May 2011 in “Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism” Breast cancer survivors may have a higher risk of falls, tamoxifen could prevent breast cancer and deaths, new guidelines urge caution with prostate cancer therapy, and early balding in men may indicate a higher prostate cancer risk.
 50 citations,
May 2011 in “Journal of Ethnopharmacology”
50 citations,
May 2011 in “Journal of Ethnopharmacology” Eclipta alba extract shows potential as an anticancer agent by inhibiting cancer cell growth and promoting cell death.
8 citations,
July 2021 in “F1000Research” Plant-based compounds might be a promising alternative for prostate cancer treatment with fewer side effects.
 October 2021 in “International journal of basic and clinical pharmacology”
October 2021 in “International journal of basic and clinical pharmacology” Excessive eyelash growth from erlotinib may indicate positive tumor response and help treat madarosis.
 November 1999 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
November 1999 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” The document concludes that there is a need for more research and regulation in dermatology, covering topics like latex allergy in children, the use of botulinum toxin, and treatments for skin conditions.
 36 citations,
January 2018 in “Burns & Trauma”
36 citations,
January 2018 in “Burns & Trauma” NSAIDs may not affect soft tissue healing but should be used carefully for bone fractures and more research is needed to understand sex differences in response.
[object Object]  25 citations,
August 1992 in “In vitro cellular & developmental biology”
25 citations,
August 1992 in “In vitro cellular & developmental biology” The new system can grow hair in the lab and test hair growth treatments.
 May 2024 in “International Journal of Nanomedicine”
May 2024 in “International Journal of Nanomedicine” Biodegradable polymers can improve cannabinoid delivery but need more clinical trials.


























