3 citations,
August 2019 in “Journal of Cancer Research and Therapeutics” Cetuximab can cause unusual hair growth and hair loss.
2 citations,
May 2020 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” A TP63 gene mutation causes significant hair loss and mild skin, nail, and tooth abnormalities.
 1 citations,
January 2022 in “Transgender health”
1 citations,
January 2022 in “Transgender health” Hormone therapy in transgender individuals can increase acne and affect hair growth and loss.
January 2016 in “Dermatology Online Journal” Hormonal therapy changes skin and hair in transgender patients, who need better researched dermatologic care.

Cross-section trichometry is an accurate method to measure hair loss and growth.
 July 1980 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
July 1980 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The conference concluded that understanding hair and nail disorders is important, iron deficiency may be linked to hair loss, and while some treatments for skin conditions are effective, they may have risks and high costs.
 June 2007 in “Advances in Dermatology and Allergology/Postępy Dermatologii i Alergologii”
June 2007 in “Advances in Dermatology and Allergology/Postępy Dermatologii i Alergologii” Finasteride is effective in stopping hair loss and promoting regrowth in most men with mild side effects.
19 citations,
January 2019 in “JAAD case reports” A medication for skin rash also unexpectedly treated hair loss in a patient.
17 citations,
December 2013 in “Dermatologic Surgery” The treatment improved hair color in most vitiligo patients without major side effects.
 16 citations,
March 2013 in “JAMA Dermatology”
16 citations,
March 2013 in “JAMA Dermatology” A cancer drug called nilotinib might cause hair loss due to inflammation around hair follicles.
 8 citations,
January 2003 in “Pharmacotherapy: The Journal of Human Pharmacology and Drug Therapy”
8 citations,
January 2003 in “Pharmacotherapy: The Journal of Human Pharmacology and Drug Therapy” Chemotherapy may cause recurring hair loss due to an autoimmune response.
 1 citations,
January 1987 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
1 citations,
January 1987 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The patient's hair loss was likely not caused by beta blockers but possibly by stress or other factors.
 November 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
November 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Tofacitinib is effective and has minor, reversible side effects for treating severe hair loss in Iran.
 December 2019 in “Pediatria i Medycyna Rodzinna”
December 2019 in “Pediatria i Medycyna Rodzinna” Alopecia areata is a hair loss condition that may be linked to stress and genetics, often requires psychological support, and has no set treatment.
 July 2015 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
July 2015 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” A woman experienced excessive hair growth after using a hair loss treatment with minoxidil.
 30 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
30 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” New criteria for diagnosing frontal fibrosing alopecia include specific scalp and eyebrow hair loss as major factors and other hair loss areas and hair analysis as minor factors.
 May 2021 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society”
May 2021 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society” A patient produced cortisol after adrenalectomy, possibly due to residual tissue or other body parts making steroids.
 21 citations,
April 2011 in “Physiological Research”
21 citations,
April 2011 in “Physiological Research” Normal levels of DHT can reduce belly fat and increase muscle, but too much can lead to hair loss, prostate issues, and possibly heart disease.
 16 citations,
February 2016 in “Gynecological Endocrinology”
16 citations,
February 2016 in “Gynecological Endocrinology” Indian women with PCOS from Delhi and Srinagar show different symptoms, with Delhi women having higher obesity and blood sugar issues, and Srinagar women showing more hair growth and testosterone levels.
 339 citations,
February 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
339 citations,
February 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Most patients with frontal fibrosing alopecia are postmenopausal women, and treatments like finasteride and dutasteride can improve or stabilize the condition.
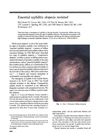 53 citations,
May 1995 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
53 citations,
May 1995 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Syphilis can cause hair loss that looks like other conditions, but it improves with treatment.
31 citations,
September 2020 in “Clinical endocrinology” Some antiandrogens may lower testosterone better than others, but it's unclear which is best for feminization in transgender women; more research is needed.
 25 citations,
November 2013 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
25 citations,
November 2013 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Many patients on new leukemia drugs had mild to moderate skin reactions.
 21 citations,
October 2017 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
21 citations,
October 2017 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Various potential triggers may be causing the rise in frontal fibrosing alopecia, and avoiding these could help stop the disease's increase.
 19 citations,
June 2015 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
19 citations,
June 2015 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” There is no cure for alopecia areata, and treatment success depends on the individual's situation.
 17 citations,
November 2018 in “Dermatology”
17 citations,
November 2018 in “Dermatology” Most patients with frontal fibrosing alopecia had facial bumps, with Hispanic/Latino and premenopausal women being more affected, suggesting a more severe condition.
 13 citations,
February 2019 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
13 citations,
February 2019 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” The document concludes that a new system using the SALT score should replace the current alopecia areata classification for better accuracy in assessing severity and prognosis.
 11 citations,
March 2016 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
11 citations,
March 2016 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Almost all patients with chronic kidney disease not yet on dialysis have at least one skin problem.
 9 citations,
September 2000 in “Obstetrics and gynecology clinics of North America”
9 citations,
September 2000 in “Obstetrics and gynecology clinics of North America” Hirsutism causes significant psychological distress in women.
7 citations,
January 2017 in “Neuromuscular Disorders” A rare autoimmune condition, Satoyoshi syndrome, can start in adults and improve with immunosuppressive treatment.






















