 May 2023 in “Materials research foundations”
May 2023 in “Materials research foundations” Nanomaterials like silver and gold can improve wound healing but need more research for safety.
 April 2012 in “CORD. Coconut research & development/CORD”
April 2012 in “CORD. Coconut research & development/CORD” Coconut leaf vermiwash improves soil health and crop yields in organic farming.
2 citations,
February 2024 in “Pharmaceutics” Chitosan scaffolds with silver nanoparticles effectively treat infected wounds and promote faster healing.
[object Object]  5 citations,
January 2019 in “Giornale italiano di dermatologia e venereologia”
5 citations,
January 2019 in “Giornale italiano di dermatologia e venereologia” Hair loss can happen after a fever caused by Rickettsia conorii infection.
1 citations,
January 2019 in “PubMed” A woman developed a hair disorder after a bone marrow transplant, which improved with treatment.
 1 citations,
August 2018 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
1 citations,
August 2018 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” A new mutation in the TMEM173 gene and a risk allele in IFIH1 cause a unique set of immune-related symptoms.
 2 citations,
March 2015 in “World journal of acupuncture-moxibustion”
2 citations,
March 2015 in “World journal of acupuncture-moxibustion” Traditional Chinese medicine techniques like catgut embedment, moxibustion, and bloodletting showed better results for treating hair loss than the drug finasteride.
 76 citations,
November 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
76 citations,
November 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Some African American women's central scalp hair loss is linked to genetics and past fungal scalp infections, with more research needed on other causes.
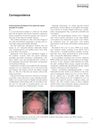 12 citations,
November 2011 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
12 citations,
November 2011 in “International Journal of Dermatology” A woman developed a scalp condition from using minoxidil, which improved with a different treatment but left scarring.
 September 2021 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
September 2021 in “Research Square (Research Square)” Not having enough or having too much of the protein Grainyhead-like 3 leads to various developmental problems.
 67 citations,
February 1983 in “The Journal of Dermatologic Surgery and Oncology”
67 citations,
February 1983 in “The Journal of Dermatologic Surgery and Oncology” Vigilon, a new wound dressing, promotes faster and better healing with less pain.
 August 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
August 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” A 90-year-old woman's hand lesion was a rare, aggressive skin cancer treated successfully with surgery.
 August 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
August 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” A 5-year-old girl with a rare skin disorder was effectively treated with skin creams instead of oral medication.
 14 citations,
June 2019 in “BMC infectious diseases”
14 citations,
June 2019 in “BMC infectious diseases” A rare fungal infection on a child's scalp was successfully treated with antifungal medication.
[object Object] 198 citations,
January 1998 in “Dermatology” The human sebocyte culture model has improved understanding of oily skin and acne, and how they can be treated.
 83 citations,
July 2008 in “Current Opinion in Chemical Biology”
83 citations,
July 2008 in “Current Opinion in Chemical Biology” The document concludes that understanding sulfation biology is crucial for creating treatments due to its importance in biological functions and disease.
 70 citations,
December 2004 in “Differentiation”
70 citations,
December 2004 in “Differentiation” The study identified and characterized new keratin genes linked to hair follicles and epithelial tissues.
61 citations,
January 2013 in “International Journal of Biological Macromolecules” Combining DHT and EDC improves the strength and stability of PADM scaffolds for tissue engineering.
 January 2016 in “Dermatology Online Journal”
January 2016 in “Dermatology Online Journal” Pregnant women with blisters should be checked for bullous impetigo.
 1 citations,
June 2010 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
1 citations,
June 2010 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Covers common skin issues in kids, their diagnosis, treatment, and need for specialist care.
 7 citations,
July 2019 in “International archives of internal medicine”
7 citations,
July 2019 in “International archives of internal medicine” Common skin conditions can greatly affect a person's mental health and social life.
 37 citations,
January 2013 in “Postepy Dermatologii I Alergologii”
37 citations,
January 2013 in “Postepy Dermatologii I Alergologii” Isotretinoin effectively reduces acne but causes dry skin, higher skin pH, more redness, and hair loss.
6 citations,
January 2013 in “Journal of Veterinary Medical Science” The dog's skin and anemia issues returned after stopping treatment for Babesia gibsoni.
 April 2021 in “Animal Bioscience”
April 2021 in “Animal Bioscience” 5-Aminolevulinic acid can help chicken sperm move better at the right amount.
 3 citations,
January 2014 in “International Journal of Medical Sciences”
3 citations,
January 2014 in “International Journal of Medical Sciences” Mice with human chymase had a higher death rate when exposed to a toxin compared to normal mice.
 January 2006 in “Elsevier eBooks”
January 2006 in “Elsevier eBooks” Cats with Feline Symmetrical Alopecia can regrow hair with proper treatment based on the specific cause, including diet, medication, or stress management.
 May 2019 in “Journal of the Dermatology Nurses’ Association”
May 2019 in “Journal of the Dermatology Nurses’ Association” Folliculitis decalvans mainly affects middle-aged African American men and is treated with antibiotics.
October 2022 in “Biomolecules” Allopregnanolone can reduce gut inflammation and normalize neurotransmitter levels after finasteride withdrawal.
 25 citations,
June 2014 in “Journal of Endocrinology/Journal of endocrinology”
25 citations,
June 2014 in “Journal of Endocrinology/Journal of endocrinology” Human sebaceous glands contain enzymes that affect androgen production and may influence sebum production and acne.
 April 2024 in “International journal of medical science and clinical research studies”
April 2024 in “International journal of medical science and clinical research studies” Effective acne management in PCOS includes hormone therapy, metformin, isotretinoin, weight loss, diet, exercise, and personalized treatment plans.
























