 3 citations,
January 2016 in “Journal of cosmetology & trichology”
3 citations,
January 2016 in “Journal of cosmetology & trichology” Taking vitamins, minerals, and amino acids can improve hair strength and quality in people with Monilethrix.
 3 citations,
November 1999 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
3 citations,
November 1999 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Examining scalp biopsies in different ways helps better diagnose hair loss types.

Eclipta alba L. (Urang-Aring) can help treat hair loss.
 May 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
May 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” LED light helps human hair root cells grow and prevents them from dying by activating specific growth pathways.
102 citations,
July 2020 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Hormones like testosterone and estrogen significantly affect hair growth and structure.
 67 citations,
September 2008 in “Dermatologic therapy”
67 citations,
September 2008 in “Dermatologic therapy” Hirsutism is excessive hair growth in women often caused by polycystic ovarian syndrome, and identifying the cause is important for managing associated health risks.
 39 citations,
March 2018 in “Archives of Dermatological Research”
39 citations,
March 2018 in “Archives of Dermatological Research” Androgens may block hair growth signals, targeting this could treat hair loss.
 10 citations,
May 1995 in “Journal of General Internal Medicine”
10 citations,
May 1995 in “Journal of General Internal Medicine” Most women with excessive hair growth have PCOS; treatment varies and focuses on preventing new hair, with electrolysis as the only permanent removal method.
 9 citations,
April 1993 in “Journal of the National Cancer Institute”
9 citations,
April 1993 in “Journal of the National Cancer Institute” Interleukin-2 treatment improved hair growth, sexual function, and reduced fungal infection in a patient with thymoma-related symptoms.
April 2012 in “Journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences” No effective treatment exists to stimulate hair growth in atrichia with papular lesions.
 6 citations,
July 2013 in “Acta Clinica Belgica”
6 citations,
July 2013 in “Acta Clinica Belgica” The document concludes that combination therapy is most effective for treating excessive hair growth in women with idiopathic hirsutism, and more research is needed to understand the condition.
 1 citations,
January 2009 in “CRC Press eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2009 in “CRC Press eBooks” Finasteride increases hair count and improves hair growth with low risk of side effects.
January 1989 in “Handbook of experimental pharmacology” Drugs can change hair growth and this is important because it can upset people.
 15 citations,
January 1988 in “Drugs”
15 citations,
January 1988 in “Drugs” The document concludes that treatments for female hair loss and excessive hair growth are temporary and not well-studied.
 April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Women with PCOS often have more hair growth, skin darkening, and acne, which are linked to hormonal and metabolic issues.
 233 citations,
November 2002 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
233 citations,
November 2002 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Creating stronger blockers for skin enzymes might lead to better treatment for conditions like acne and excessive hair growth.
 122 citations,
November 2010 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
122 citations,
November 2010 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Male pattern baldness involves hormones and cell signals affecting hair growth.
 54 citations,
June 1985 in “American Journal of Dermatopathology”
54 citations,
June 1985 in “American Journal of Dermatopathology” Minoxidil helps grow longer, thicker hair in bald scalps of stumptailed macaques, and early treatment is more effective.
 28 citations,
May 1986 in “Clinics in endocrinology and metabolism”
28 citations,
May 1986 in “Clinics in endocrinology and metabolism” New compounds may soon be tested to treat excessive hair growth in women.
 10 citations,
January 2003 in “Seminars in reproductive medicine”
10 citations,
January 2003 in “Seminars in reproductive medicine” The article explains how to identify and treat excessive hair growth in women, which can be distressing and may signal other health problems.
 5 citations,
January 2010 in “The anatomical record”
5 citations,
January 2010 in “The anatomical record” Most dogs have hair whorls on their chest and limbs, with shelter dogs and short-haired dogs having more chest whorls.
 100 citations,
September 2017 in “Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology”
100 citations,
September 2017 in “Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology” Male hormones and their receptors play a key role in hair loss and skin health, with potential new treatments being explored.
 59 citations,
August 1998 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
59 citations,
August 1998 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Genetics and hormones cause hair loss; finasteride treats it safely.
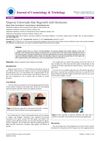 January 2017 in “Journal of cosmetology & trichology”
January 2017 in “Journal of cosmetology & trichology” A man with severe hair loss regrew hair after hormone treatment.
 17 citations,
October 2003 in “Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research”
17 citations,
October 2003 in “Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research” The gene SDR5A1 is found in scalp hair of both hirsute and normal individuals, but it does not explain differences in hair growth.
 30 citations,
December 1999 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
30 citations,
December 1999 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Oral ivermectin effectively cured scabies with minimal side effects, and finasteride promoted hair growth in men with hair loss.
 82 citations,
January 2000 in “Hormone Research in Paediatrics”
82 citations,
January 2000 in “Hormone Research in Paediatrics” DHEA stimulates skin oil glands and could help postmenopausal women, with potential for acne and excessive hair growth treatments.
1 citations,
November 2010 in “Obstetrics and gynecology clinics of North America” Gynecologists can make more money by offering laser hair removal because it's popular.
 53 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
53 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Cancer treatments often cause hair disorders, significantly affecting patients' quality of life, and better management methods are needed.
 30 citations,
April 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology”
30 citations,
April 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology” The article concludes that developing in vitro models for human hair structures is important for research and reducing animal testing, but there are challenges like obtaining suitable samples and the models' limitations.


























