11 citations,
January 2018 in “Jaypee's international journal of clinical pediatric dentistry” Papillon-Lefèvre Syndrome causes early tooth loss and skin issues, needing early dental diagnosis.
 7 citations,
January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology”
7 citations,
January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology” A man with Woolly Hair Syndrome had very curly, fragile hair, and doctors used a special scalp examination to diagnose him without invasive tests.
7 citations,
May 2021 in “Animal Genetics” The CORIN gene variant causes the golden color in Siberian cats.
4 citations,
January 2013 in “International Journal of Trichology” Monilethrix has no effective treatment, but avoiding hair trauma helps manage it.
 1 citations,
February 2013 in “Clinical pediatrics”
1 citations,
February 2013 in “Clinical pediatrics” The baby’s hair loss was due to a rare genetic condition, not treatable by usual methods.

CaBP1 and CaBP2 are important for continuous hearing by preventing inactivation of calcium currents in ear cells, with CaBP2 also able to restore hearing when reintroduced.
 September 2023 in “International journal of science and healthcare research”
September 2023 in “International journal of science and healthcare research” Genetic testing is crucial for diagnosing congenital atrichia, a rare condition causing irreversible hair loss.
 July 2024 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
July 2024 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Hair loss in certain mice is linked to changes in keratin-related genes.
 September 2022 in “IP Indian journal of clinical and experimental dermatology”
September 2022 in “IP Indian journal of clinical and experimental dermatology” An 8-year-old girl has a rare genetic disorder causing complete, irreversible hair loss and skin bumps.

The chapter explains that there are many genetic skin disorders affecting skin cell formation, including both common and rare types.
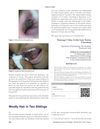 January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology”
January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology” Two siblings have a rare genetic condition causing curly, coarse hair.
 July 2005 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
July 2005 in “British Journal of Dermatology” New gene mutations linked to skin conditions were found, bacteria and chemicals may worsen acne, a dog mutation could exist in humans, virus-like elements might be involved in psoriasis, and a vitamin D3 treatment doesn't prevent chemotherapy-related hair loss.
12 citations,
July 2004 in “Molecular genetics and genomics” A new mouse mutation causes skin and hair defects due to a gene change.
13 citations,
June 2006 in “Fertility and Sterility” Nonclassic 21-hydroxylase deficiency is a common, treatable genetic disorder causing reversible symptoms like acne and hair loss.
 August 2021 in “Journal of medical science and clinical research”
August 2021 in “Journal of medical science and clinical research” An infant with seizures and hair loss was diagnosed with biotinidase deficiency and treated successfully with biotin.
 32 citations,
January 2017 in “Orphanet journal of rare diseases”
32 citations,
January 2017 in “Orphanet journal of rare diseases” FOXN1 gene mutations cause a rare, severe immune disease treatable with cell or tissue transplants.
8 citations,
January 2011 in “International journal of trichology” Accurate diagnosis of APL is crucial to avoid unnecessary treatments.
 April 2020 in “Journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences”
April 2020 in “Journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences” A one-year-old child with a genetic condition had symptoms improved by treating zinc deficiency.
April 2012 in “Journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences” No effective treatment exists to stimulate hair growth in atrichia with papular lesions.
 December 2024 in “Journal of Clinical Research in Pediatric Endocrinology”
December 2024 in “Journal of Clinical Research in Pediatric Endocrinology” 21-hydroxylase deficiency causes hormone imbalances leading to various symptoms, and diagnosis involves clinical and genetic tests.
 January 2023 in “International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics”
January 2023 in “International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics” A rare genetic disease causes rickets and often hair loss in young children, which can improve with specific treatments.
38 citations,
September 1997 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” A mutation in mice causes hair loss and skin issues due to a defect in a gene affecting cell adhesion.
31 citations,
September 2003 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Vitamin D-dependent rickets Type II causes bone problems and hair loss, and doesn't improve with Vitamin D treatment.
 5 citations,
January 1970 in “Journal of Nepal Paediatric Society”
5 citations,
January 1970 in “Journal of Nepal Paediatric Society” Hair loss can be a key sign of a rare type of rickets when vitamin D treatment doesn't work and advanced tests aren't available.
 1 citations,
September 2018 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
September 2018 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” A boy with GAPO syndrome had hair loss similar to male pattern baldness without hormone issues, possibly due to skin or blood vessel problems.
 December 2024 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology”
December 2024 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology” Dermoscopy is useful for diagnosing Atrichia with Papular Lesions in children without needing a biopsy.
43 citations,
April 2010 in “Clinical genetics” Truncating mutations in the C2orf37 gene cause Woodhouse–Sakati syndrome.
 39 citations,
January 2015 in “Annals of dermatology/Annals of Dermatology”
39 citations,
January 2015 in “Annals of dermatology/Annals of Dermatology” Three new types of a skin blistering disease were found, caused by specific gene mutations.
 6 citations,
January 2014 in “Journal of pediatric endocrinology & metabolism/Journal of pediatric endocrinology and metabolism”
6 citations,
January 2014 in “Journal of pediatric endocrinology & metabolism/Journal of pediatric endocrinology and metabolism” Three siblings with a genetic form of rickets showed different symptoms of the disease.
 3 citations,
December 2021 in “Frontiers in endocrinology”
3 citations,
December 2021 in “Frontiers in endocrinology” A new mutation in the DCAF17 gene was found in a Chinese family, causing Woodhouse-Sakati syndrome and diabetes.



















