 January 2025 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
January 2025 in “The Journal of Dermatology” Certain patient traits can predict better hair regrowth with baricitinib in severe alopecia areata.
 January 2025 in “SKIN The Journal of Cutaneous Medicine”
January 2025 in “SKIN The Journal of Cutaneous Medicine” Baricitinib treatment for severe alopecia areata shows significant improvement by 52 weeks, especially in very severe cases.
 July 2024 in “Medical alphabet”
July 2024 in “Medical alphabet” Betamethasone injections are more effective than Clobetasol for treating alopecia areata in children.
 April 2024 in “Liječnički vjesnik”
April 2024 in “Liječnički vjesnik” Modern treatments can effectively regrow hair and improve life for people with alopecia areata.
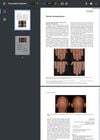 March 2024 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
March 2024 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Baricitinib improved nail condition and hair regrowth in a patient with alopecia and nail abnormalities.
 February 2024 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
February 2024 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Using a laser with bimatoprost solution works better for hair regrowth in alopecia areata than bimatoprost alone.
 January 2024 in “Skin Research and Technology”
January 2024 in “Skin Research and Technology” Oral tofacitinib may be an effective future treatment for children with severe alopecia areata, but more research is needed.
 November 2023 in “Dermatologica sinica/Zhōnghuá pífūkē yīxué zázhì”
November 2023 in “Dermatologica sinica/Zhōnghuá pífūkē yīxué zázhì” Upadacitinib helped regrow hair in a severe alopecia areata patient but stopping treatment caused hair loss to return.
 October 2023 in “Applied materials today”
October 2023 in “Applied materials today” New treatment for hair loss using special microneedles shows promise in reducing inflammation and promoting hair growth.
Intralesional methotrexate effectively treats alopecia areata by reducing TNF-α levels, leading to hair regrowth.
 May 2023 in “International Journal of Trichology”
May 2023 in “International Journal of Trichology” Tofacitinib may be an effective and safe treatment for hair loss in teenagers with alopecia areata.
 February 2023 in “Archives of Dermatological Research”
February 2023 in “Archives of Dermatological Research” Laser treatment, especially when combined with other therapies, is effective for hair regrowth in alopecia areata.
 January 2023 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine”
January 2023 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine” New treatments for sudden hair loss include oral medications and a special laser, both showing promise in hair regrowth.
 July 2022 in “المجلة العراقية للصيدلة”
July 2022 in “المجلة العراقية للصيدلة” Azelaic acid 20% cream works well for treating scalp alopecia areata and can be an alternative to clobetasol ointment.
 June 2022 in “Pakistan Journal of Medical and Health Sciences”
June 2022 in “Pakistan Journal of Medical and Health Sciences” Topical clobetasol propionate 0.05% ointment is more effective in promoting hair regrowth in patients with alopecia areata than topical tacrolimus 0.1% ointment.
Intralesional steroids are the most effective treatment for alopecia areata.
 August 2017 in “International journal of research in dermatology”
August 2017 in “International journal of research in dermatology” 0.05% betamethasone dipropionate is the most effective treatment for mild alopecia areata.
 June 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
June 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Tofacitinib is effective and safe for treating severe alopecia areata and related conditions.
January 2016 in “Indian Journal of Paediatric Dermatology” The treatment is effective and safe for severe alopecia areata in children, but not for total or universal hair loss.
 May 2015 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
May 2015 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Both treatments help with hair regrowth in alopecia areata, but azathioprine has milder side effects than betamethasone.
No cure exists for alopecia areata; treatments aim to manage symptoms.
February 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Combining microneedling with either vitamin D3 or bimatoprost improves hair regrowth more than microneedling alone.
October 2022 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Both treatments for resistant alopecia areata were equally effective.
83 citations,
June 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Topical JAK inhibitors may help children with alopecia areata regrow hair.
 80 citations,
October 1983 in “BMJ”
80 citations,
October 1983 in “BMJ” Minoxidil helps hair regrowth in alopecia patients, with 16 having good results and no side effects.
 79 citations,
September 2009 in “Pediatric dermatology”
79 citations,
September 2009 in “Pediatric dermatology” The 308-nm Excimer laser is effective and safe for treating patchy alopecia areata in children.
48 citations,
July 1998 in “Pediatric Dermatology” Monthly oral corticosteroid pulses effectively treat widespread alopecia areata in young patients.
45 citations,
July 2008 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Sulfasalazine may help treat persistent alopecia areata.
 37 citations,
October 2017 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
37 citations,
October 2017 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Oral tofacitinib shows promise in treating atopic dermatitis and alopecia areata, but only slight improvement in vitiligo.
37 citations,
September 2009 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Diphencyprone (DPC) is an effective and safe long-term treatment for alopecia areata, especially with maintenance therapy.



















