 4 citations,
January 2023 in “Frontiers in Medicine”
4 citations,
January 2023 in “Frontiers in Medicine” Zinc is important for skin health, and supplements can help treat various skin and hair disorders, but more research is needed for conditions like psoriasis and vitiligo.
 36 citations,
June 2017 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
36 citations,
June 2017 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” The consensus document recommends a comprehensive treatment plan for Hidradenitis Suppurativa, including various medications, surgery, lifestyle changes, and the need for more research and resources.
 2 citations,
January 2014 in “Springer eBooks”
2 citations,
January 2014 in “Springer eBooks” The book details skin conditions in older adults, their link to mental health, cancer treatment importance, hair loss remedies, and managing autoimmune and itchy skin.
April 2024 in “Journal of clinical medicine” Recognizing specific skin features helps diagnose and manage lupus erythematosus effectively.
 146 citations,
January 2004 in “Hormones”
146 citations,
January 2004 in “Hormones” Human skin acts like a hormone-producing organ, making and managing various hormones important for skin and hair health.
July 2017 in “Journal of the Dermatology Nurses’ Association” The convention highlighted knowledge sharing, networking, and the importance of active participation in dermatology.
 January 2020 in “Open Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology”
January 2020 in “Open Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology” All women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) in a study had at least one skin disorder, with the most common being excessive hair growth, acne, dark skin patches, hair loss, and oily skin.
 116 citations,
December 2017 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology”
116 citations,
December 2017 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology” Adult female acne treatment should be personalized, considering individual preferences and pregnancy, using various topical and oral medications while managing side effects and resistance.
 6 citations,
January 2017 in “Dermato-endocrinology”
6 citations,
January 2017 in “Dermato-endocrinology” ADT-G may be a useful indicator of increased androgen levels in women with acne and can be lowered with certain birth control pills.
 4 citations,
January 2011 in “Current problems in dermatology”
4 citations,
January 2011 in “Current problems in dermatology” At-home laser and light devices can safely reduce acne and hair growth when used correctly but are less effective than professional treatments.
 33 citations,
January 2021 in “Aesthetic Surgery Journal”
33 citations,
January 2021 in “Aesthetic Surgery Journal” Low-Level Light Therapy (LLLT) is a safe and effective method for skin rejuvenation, acne treatment, wound healing, body contouring, and hair growth, but more well-designed trials are needed for confirmation.
9 citations,
June 2020 in “Trials” The trial aims to test if spironolactone is an effective acne treatment for women without the side effects of current treatments.
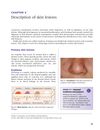
The document explains different types of skin lesions and their characteristics, causes, and related conditions.
 October 2016 in “Elsevier eBooks”
October 2016 in “Elsevier eBooks” Common noncancerous skin diseases have various treatments, including topical applications, light therapy, surgery, and medications, with psychological support being important.
35 citations,
October 2019 in “Journal of pediatric health care” Children with darker skin tones can have specific skin conditions that need tailored treatments.
 July 2019 in “Journal of case reports and scientific images”
July 2019 in “Journal of case reports and scientific images” A 23-year-old woman has Acne Vulgaris, which causes different types of skin bumps and possible scarring.
 14 citations,
October 2019 in “International Journal of Women's Health”
14 citations,
October 2019 in “International Journal of Women's Health” Menopausal acne is treated with medications and lifestyle changes, but careful choice is needed due to side effects.
 January 2024 in “International Journal of Dermatology Venereology and Leprosy Sciences”
January 2024 in “International Journal of Dermatology Venereology and Leprosy Sciences” Patients with acne vulgaris have lower serum irisin levels.
 78 citations,
February 2011 in “Canadian Medical Association Journal”
78 citations,
February 2011 in “Canadian Medical Association Journal” Acne treatment varies, with topical and systemic therapies effective, and more research needed on treatment order and long-term effects.
 June 2023 in “Benha Journal of Applied Sciences”
June 2023 in “Benha Journal of Applied Sciences” Acne is caused by multiple types of bacteria.
 18 citations,
August 2011 in “Clinical Drug Investigation”
18 citations,
August 2011 in “Clinical Drug Investigation” Low-dose isotretinoin combined with pulsed azithromycin cleared acne in most patients, with mild side effects.
 15 citations,
January 2016 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
15 citations,
January 2016 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Start acne treatment early to prevent scarring, consider antibiotic resistance, use maintenance therapy, and manage side effects carefully.
 April 2024 in “International journal of women's health”
April 2024 in “International journal of women's health” Adult female acne is a complex condition that can worsen with menopause, requiring holistic treatment and tailored skincare at different life stages.
 9 citations,
April 2021 in “Expert opinion on pharmacotherapy”
9 citations,
April 2021 in “Expert opinion on pharmacotherapy” Clascoterone is a new, effective, and safe acne treatment without systemic side effects.
 November 2015 in “International journal of science and research”
November 2015 in “International journal of science and research” Adult acne is mostly inflammatory, affects women more, and often scars, needing good treatment to prevent damage.
 76 citations,
November 2009 in “Medical Clinics of North America”
76 citations,
November 2009 in “Medical Clinics of North America” Hormones, especially androgens, play a key role in acne, which can be a symptom of systemic diseases like PCOS and may require targeted treatment.
 11 citations,
February 2003 in “Baillière's best practice & research. Clinical obstetrics & gynaecology/Baillière's best practice and research in clinical obstetrics and gynaecology”
11 citations,
February 2003 in “Baillière's best practice & research. Clinical obstetrics & gynaecology/Baillière's best practice and research in clinical obstetrics and gynaecology” Acne and increased body hair in teenage girls are normal but severe cases may need hormone evaluation and treatment can prevent diabetes linked to PCO.
 11 citations,
January 1998 in “Dermatology”
11 citations,
January 1998 in “Dermatology” Isotretinoin effectively treated severe acne in HIV-positive women, with improved skin and CD4 counts, but some experienced side effects like skin dryness and hair loss.
 10 citations,
December 1996 in “Fertility and Sterility”
10 citations,
December 1996 in “Fertility and Sterility” Women with acne have lower levels of a specific hormone marker than women without acne.
 5 citations,
January 2014 in “Current Dermatology Reports”
5 citations,
January 2014 in “Current Dermatology Reports” Many adult women suffer from persistent or late-onset acne, and while various treatments exist, finding the right one can be challenging.


























