 63 citations,
May 2017 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
63 citations,
May 2017 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” People with alopecia areata often have lower levels of vitamin D, zinc, and folate, but more research is needed to understand if supplements can help treat it.
 62 citations,
October 2016 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
62 citations,
October 2016 in “Dermatologic Therapy” PRP more effective than minoxidil 5% for treating alopecia areata.
[object Object]  62 citations,
June 2015 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
62 citations,
June 2015 in “The Journal of Dermatology” People with alopecia areata have more Th17 cells and fewer Treg cells, which may be key to the condition's development.
62 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” New genetic discoveries may lead to better treatments for alopecia areata.
62 citations,
July 2013 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Alopecia areata patients have higher oxidative stress and lower antioxidant levels.
 61 citations,
September 2010 in “Genomics”
61 citations,
September 2010 in “Genomics” The study found that immune responses disrupt hair growth cycles, causing hair loss in alopecia areata.
61 citations,
June 2010 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Anti-TNF-α therapy may increase the risk of developing alopecia areata, especially in those with a history of autoimmune disease.
 60 citations,
September 2015 in “Expert Review of Clinical Immunology”
60 citations,
September 2015 in “Expert Review of Clinical Immunology” Lymphocytes, especially CD8+ T cells, play a key role in causing alopecia areata, and targeting them may lead to new treatments.
 60 citations,
January 1987 in “Dermatology”
60 citations,
January 1987 in “Dermatology” Alopecia areata may appear differently depending on the individual's type of hair loss and scalp condition.
 59 citations,
September 2008 in “Experimental dermatology”
59 citations,
September 2008 in “Experimental dermatology” Both mouse and rat models are effective for testing alopecia areata treatments.
 58 citations,
January 2018 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology”
58 citations,
January 2018 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology” Alopecia significantly lowers women's quality of life, with psychological and social challenges, highlighting the importance of early treatment and support.
 58 citations,
January 2015 in “International Journal of Trichology”
58 citations,
January 2015 in “International Journal of Trichology” Platelet-rich plasma, which carries growth factors, could be a promising treatment for non-scarring hair loss, promoting hair growth and density with no major side effects.
 57 citations,
April 2019 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement”
57 citations,
April 2019 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” Alopecia areata involves immune system imbalances that may lead to depression and anxiety.
[object Object]  56 citations,
January 2021 in “Clinical and Experimental Medicine”
56 citations,
January 2021 in “Clinical and Experimental Medicine” The document concludes that while there are various treatments for Alopecia Areata, there is no cure, and individualized treatment plans are essential due to varying effectiveness.
 56 citations,
January 2019 in “Skin appendage disorders”
56 citations,
January 2019 in “Skin appendage disorders” The most common hair loss type at specialist clinics is androgenetic alopecia, especially in younger men, followed by alopecia areata and telogen effluvium, with differences seen across regions.
56 citations,
October 2016 in “Journal of dermatological science” New insights into the causes and treatments for the autoimmune hair loss condition Alopecia areata have been made.
56 citations,
June 2010 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology” Coudability hairs are useful markers for alopecia areata activity.
55 citations,
October 2019 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology” The review suggests that other immune cells besides CD8+ T cells may contribute to alopecia areata and that targeting regulatory cell defects could improve treatment.
55 citations,
April 2015 in “BMC medicine” Stem Cell Educator therapy helps regrow hair and improve life quality in alopecia areata patients.
 54 citations,
September 2019 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
54 citations,
September 2019 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Tofacitinib is somewhat effective for alopecia areata, but more research is needed on its safety and long-term effects.
53 citations,
July 2018 in “Drug design, development and therapy” Janus kinase inhibitors show promise in treating alopecia areata but need better topical formulations.
 53 citations,
January 2018 in “JAAD case reports”
53 citations,
January 2018 in “JAAD case reports” Dupilumab for eczema may cause hair loss.
 53 citations,
March 2014 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine”
53 citations,
March 2014 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine” The document explains different types of hair loss, their causes, and treatments, and suggests future research areas.
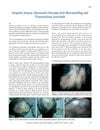 53 citations,
January 2014 in “Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery”
53 citations,
January 2014 in “Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery” Microneedling combined with triamcinolone can safely stimulate faster hair regrowth in people with Alopecia Areata.
53 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic therapy” Alopecia areata is a skin condition causing hair loss, and its exact cause is unknown, but it may involve biological mechanisms.
 52 citations,
March 2010 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
52 citations,
March 2010 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Alopecia areata shows a unique type 1 interferon signature, suggesting potential treatment by targeting this pathway.
 51 citations,
January 2012 in “Annals of dermatology/Annals of Dermatology”
51 citations,
January 2012 in “Annals of dermatology/Annals of Dermatology” A boy with alopecia regrew hair using a vitamin D cream after other treatments failed.
 51 citations,
December 2011 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
51 citations,
December 2011 in “The Journal of Dermatology” New treatments for severe hair loss often fail, but some patients see hair regrowth with specific therapies, and treatment should be tailored to the individual's situation.
 49 citations,
April 2000 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
49 citations,
April 2000 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Despite progress in treatment, the exact cause of Alopecia areata is still unknown.
48 citations,
April 2021 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Topical corticosteroids are the best initial treatment for children's alopecia areata.




















