 11 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
11 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Stopping JAK inhibitor treatment for hair loss can lead to worse hair loss than before the treatment.
 10 citations,
September 2014 in “European Journal of Dermatology”
10 citations,
September 2014 in “European Journal of Dermatology” A woman's hair loss worsened after starting hepatitis C treatment due to immune changes in her hair follicles.
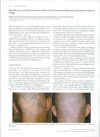 10 citations,
January 2010 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
10 citations,
January 2010 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Light therapy can effectively treat vitiligo and hair loss caused by a specific medication.
 3 citations,
January 2021 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
3 citations,
January 2021 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” The document concludes that changing the scalp's microbiome might be a new way to treat hair loss.
 3 citations,
April 2019 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment”
3 citations,
April 2019 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” Caffeine shows promise for treating some types of hair loss, but more research is needed.
 2 citations,
January 2019
2 citations,
January 2019 The document concludes that autoimmune skin disorders are treated with corticosteroids and immunosuppressive drugs.
 2 citations,
January 1997 in “Archives of Dermatology”
2 citations,
January 1997 in “Archives of Dermatology” Alopecia areata can regrow hair in a pattern similar to androgenetic alopecia.
 1 citations,
April 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
1 citations,
April 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Melanocyte-associated antigens may play a key role in alopecia areata and could be targets for new treatments.
 1 citations,
January 2013 in “International Journal of Trichology”
1 citations,
January 2013 in “International Journal of Trichology” The conference discussed various hair disorders and treatments, including the use of topical steroids, high doses of cetrizine, and hair grafting, as well as the psychological impact of hair loss.
 January 2024 in “American journal of clinical dermatology”
January 2024 in “American journal of clinical dermatology” Ritlecitinib is safe and well-tolerated for treating alopecia areata in patients aged 12 and older.

Upadacitinib effectively treated a patient with multiple inflammatory conditions.
 October 2023 in “Regular and Young Investigator Award Abstracts”
October 2023 in “Regular and Young Investigator Award Abstracts” Baricitinib treatment helped reduce hair loss symptoms in mice by decreasing inflammation-related immune cells.
 August 2023 in “International journal of research in dermatology”
August 2023 in “International journal of research in dermatology” Janus kinase inhibitors are effective and generally safe for treating hair loss in adults with alopecia areata.
 January 2023 in “Rossijskij žurnal kožnyh i veneričeskih boleznej”
January 2023 in “Rossijskij žurnal kožnyh i veneričeskih boleznej” New treatments for child hair loss due to immune issues are effective but not yet officially approved.

A teenager had both alopecia areata and vitiligo, which are rare to occur together.
 March 2021 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
March 2021 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” The microbiome may be linked to hair loss and could be a target for new treatments.
 June 2019 in “Journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences”
June 2019 in “Journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences” Dermoscopy is useful for tracking alopecia areata treatment, with yellow dots and new vellus hairs being good indicators of hair regrowth.
 April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The role of γδT-cells in causing alopecia areata remains unclear.
 April 2003 in “Experimental Dermatology”
April 2003 in “Experimental Dermatology” The workshop highlighted the genetic links and psychological impacts of hair loss and skin disorders.
 205 citations,
April 2013 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
205 citations,
April 2013 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Platelet-rich plasma treatment significantly increased hair regrowth and decreased discomfort in alopecia patients, making it a potentially better and safer treatment option.
 185 citations,
June 2014 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
185 citations,
June 2014 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” A man with severe hair loss and skin disease regrew his hair with no side effects after taking tofacitinib.
 182 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
182 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Some treatments can help with a hair loss condition called alopecia areata, but none ensure lasting results; choices depend on the person, with JAK inhibitors showing promise for severe cases.
 136 citations,
February 2017 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
136 citations,
February 2017 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” PRP treatment improves hair growth, and the device used can affect results, with some being more effective.
 95 citations,
November 2018 in “Australasian journal of dermatology”
95 citations,
November 2018 in “Australasian journal of dermatology” Alopecia areata treatment varies, with no optimal method established yet.
 87 citations,
December 2016 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement”
87 citations,
December 2016 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” Cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors may develop alopecia, but some hair regrowth is possible with treatment.
 74 citations,
April 2005 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
74 citations,
April 2005 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Minoxidil and finasteride are effective for male hair loss, minoxidil for female hair loss, and various treatments like corticosteroids work for alopecia areata; treatment should be tailored to the individual.
 70 citations,
April 2016 in “Experimental Dermatology”
70 citations,
April 2016 in “Experimental Dermatology” A patient with alopecia areata regrew hair after taking tofacitinib and showed changes in certain blood and skin markers.
 58 citations,
January 2018 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology”
58 citations,
January 2018 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology” Alopecia significantly lowers women's quality of life, with psychological and social challenges, highlighting the importance of early treatment and support.
 56 citations,
January 2021 in “Clinical and Experimental Medicine”
56 citations,
January 2021 in “Clinical and Experimental Medicine” The document concludes that while there are various treatments for Alopecia Areata, there is no cure, and individualized treatment plans are essential due to varying effectiveness.
 56 citations,
January 2019 in “Skin appendage disorders”
56 citations,
January 2019 in “Skin appendage disorders” The most common hair loss type at specialist clinics is androgenetic alopecia, especially in younger men, followed by alopecia areata and telogen effluvium, with differences seen across regions.






























