 28 citations,
January 2013 in “Stem cells”
28 citations,
January 2013 in “Stem cells” Certain human skin cells marked by CD44 and ALDH are rich in stem cells capable of long-term skin renewal.
 28 citations,
July 2007 in “Development”
28 citations,
July 2007 in “Development” TAF4 is important for skin cell growth and helps prevent skin cancer in mice.
27 citations,
November 2007 in “Genomics” Mutations in specific keratin genes cause improper hair structure in mice due to faulty keratin protein assembly.
 18 citations,
November 2014 in “Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry”
18 citations,
November 2014 in “Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry” Brazilian propolis was found to speed up hair growth in mice by increasing the growth of skin cells that form hair.
 17 citations,
July 2018 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science”
17 citations,
July 2018 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science” Keratin-based particles safely improve hair strength, smoothness, and heat protection.
7 citations,
July 2019 in “Animals” The KRTAP21-1 gene affects wool yield and can help improve wool production.
 7 citations,
February 1998 in “Polymer journal”
7 citations,
February 1998 in “Polymer journal” Keratin structure in hair is stable at pH 5-6 but disrupts between pH 6-7.
 3 citations,
June 2017 in “Journal of Biomaterials Applications”
3 citations,
June 2017 in “Journal of Biomaterials Applications” Keratin extract from human hair was found to promote hair growth in mice.
1 citations,
January 2023 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Rabbits with Sarcoptes scabiei had thicker skin, cell death, and skin hardening.
 March 2023 in “Asian journal of beauty & cosmetology”
March 2023 in “Asian journal of beauty & cosmetology” Keratin pretreatment improves the quality of damaged hair during perming.
 June 2020 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
June 2020 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Scientists successfully grew mini hair follicles using human skin cells, which could help treat baldness.

Human hair keratins can self-assemble and support cell growth, useful for biomedical applications.
January 2007 in “The FASEB journal” Human hair keratins help nerve regeneration and support Schwann cell activity.
8 citations,
October 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” MR antagonists may improve skin health and wound healing, especially in aging.
 49 citations,
August 2004 in “The FASEB Journal”
49 citations,
August 2004 in “The FASEB Journal” Mice with human skin protein K8 had more skin problems and cancer.
 5 citations,
September 2022 in “Antioxidants”
5 citations,
September 2022 in “Antioxidants” A substance from Caulerpa racemosa seaweed may protect against skin damage caused by air pollution by reducing oxidative stress and cell death.
2 citations,
December 2023 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Understanding keratinization is crucial for treating skin conditions like ichthyoses and psoriasis.
 2 citations,
December 2016 in “Experimental cell research”
2 citations,
December 2016 in “Experimental cell research” The research found a way to identify and study skin cells with stem cell traits, revealing they behave differently in culture and questioning current stemness assessment methods.
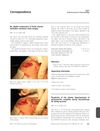 2 citations,
August 2013 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
2 citations,
August 2013 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Chemotherapy improved a girl's painful foot condition linked to pachyonychia congenita.
 September 2022 in “JAAD case reports”
September 2022 in “JAAD case reports” The man has a genetic skin condition called pachyonychia congenita.
 April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Researchers fixed gene mutations causing a skin disease in stem cells, which then improved skin grafts in mice.
April 2019 in “C&EN global enterprise” A microneedle patch can help hair regrow.
 August 2004 in “Journal of the American College of Surgeons”
August 2004 in “Journal of the American College of Surgeons” Dermagraft and Dermalogen had a lot of granulation, while Alloderm, Integra, and ADM had good blood vessel growth for skin healing.
 130 citations,
August 2015 in “Experimental Dermatology”
130 citations,
August 2015 in “Experimental Dermatology” Human hair follicle organ culture is a useful model for hair research with potential for studying hair biology and testing treatments.
 107 citations,
December 2013 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
107 citations,
December 2013 in “International Journal of Dermatology” The document concludes that hair is complex, with a detailed growth cycle, structure, and clinical importance, affecting various scientific and medical fields.
 78 citations,
April 1994 in “Archives of dermatology”
78 citations,
April 1994 in “Archives of dermatology” The study found that Keratosis Pilaris Atrophicans is a genetic skin condition that starts in childhood, involves inflammation and scarring, and current treatments are only somewhat effective.
 41 citations,
October 2008 in “The American journal of pathology”
41 citations,
October 2008 in “The American journal of pathology” Blocking a specific protein signal can make hair grow on mouse nipples.
 32 citations,
December 2018 in “Cytokine”
32 citations,
December 2018 in “Cytokine” Type I interferons play a key role in the development of various skin diseases.
 6 citations,
September 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
6 citations,
September 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Using special RNA to target a mutant gene fixed hair problems in mice.
 4 citations,
October 2017 in “Advances in tissue engineering & regenerative medicine”
4 citations,
October 2017 in “Advances in tissue engineering & regenerative medicine” Researchers created a potential skin substitute using a biodegradable mat that supports skin cell growth and layer formation.























