Update on Medical Management of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
September 2008
in “
UK vet. Companion animal
”
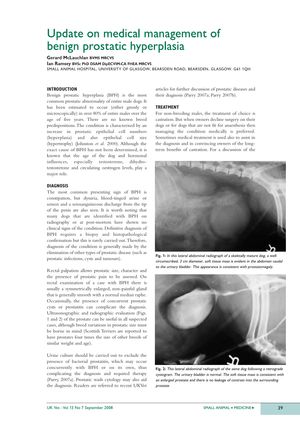
TLDR Castration is preferred for non-breeding male dogs with BPH, but other treatments are available with specific pros and cons.
The document reviewed the medical management of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) in dogs, noting that castration was preferred for non-breeding males. For those unsuitable for surgery, treatments included delmadinone acetate, osaterone, and finasteride, each with specific benefits and side effects. Delmadinone could cause polyuria and polydipsia, osaterone was effective but might cause polyphagia and vomiting, and finasteride reduced prostate size without affecting semen quality but was contraindicated in breeding animals. Other treatments like GnRH agonists and flutamide were less commonly used. The document concluded that while various medical treatments were available, each had specific advantages and potential side effects.



