A Case of Rosacea Fulminans During Pregnancy With Review of the Literature
October 2023
in “
Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft
”
TLDR Pregnancy can trigger severe rosacea, which may be treated with antibiotics and steroids, but there's no clear treatment guideline.
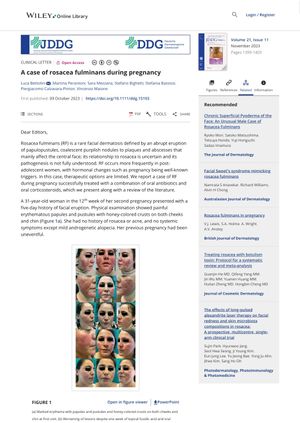
The document discusses a case of a 31-year-old pregnant woman who developed rosacea fulminans (RF) during her 12th week of pregnancy and was successfully treated with oral antibiotics and corticosteroids. Post-pregnancy, a flare-up was treated with isotretinoin, clearing the lesions within a month. The document also reviews 27 other cases of RF during pregnancy, indicating that pregnancy, especially the first trimester, can trigger RF. Treatment is challenging and often requires systemic steroids and macrolides. Nine cases reported improvement with an average initial prednisone dose of 35.5 mg daily. Early diagnosis and prompt management are crucial to reduce the lesion's extension and sequelae. However, clear dosing recommendations for RF during pregnancy are lacking.




