TLDR A woman got a scalp condition from using latanoprost, but it improved after stopping the drug and starting other treatments.
A 61-year-old woman developed erosive pustular dermatosis of the scalp (EPDS) after using latanoprost, which she was taking for mild frontotemporal androgenetic alopecia. Following the application of a 0.1% ternary solution of latanoprost, she experienced eroded, pustular, and crusted lesions on her scalp. Physical and histologic examinations confirmed the diagnosis of EPDS, characterized by pustules, erosions, scales, and a loss of normal collagen architecture around hair follicles. Upon discontinuing latanoprost and starting treatment with methylprednisolone, zinc sulphate, and clobetasol propionate, her symptoms resolved after 6 weeks, although she had residual scarring alopecia. She remained symptom-free at the 30-week follow-up.
 21 citations
,
January 2015 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
21 citations
,
January 2015 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Latanoprost may cause scalp inflammation and delayed healing.
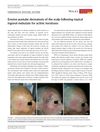 9 citations
,
July 2017 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
9 citations
,
July 2017 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Two elderly men developed scalp inflammation after using a gel for skin lesions, which healed with treatment except for some permanent hair loss.
 21 citations
,
January 2015 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
21 citations
,
January 2015 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Latanoprost may cause scalp inflammation and delayed healing.
 1 citations
,
December 2022 in “Life”
1 citations
,
December 2022 in “Life” Topical corticosteroids are the main treatment for Erosive Pustular Dermatosis, but recurrence is common after stopping treatment.
 1 citations
,
October 2013 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
1 citations
,
October 2013 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” Customized medications made through compounding can be beneficial for various skin conditions but require careful regulation and collaboration between doctors and pharmacists.
 53 citations
,
February 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
53 citations
,
February 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The conclusion is that high-potency steroids or tacrolimus are effective treatments for erosive pustular dermatosis of the scalp.





