Hair Loss Due to Electromagnetic Radiation from Overuse of Cell Phone
January 2016
in “
Journal of cosmetology & trichology
”
TLDR Excessive cell phone use may cause hair loss due to electromagnetic radiation.
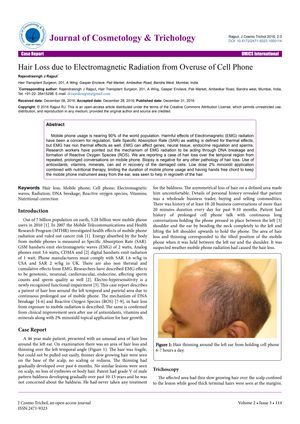
In 2016, a case report documented a 46-year-old male who developed hair loss around his left ear, which was linked to the excessive use of a mobile phone and the electromagnetic radiation it emitted. The location of the hair loss matched where the phone was frequently held during long business calls. After ruling out other causes through a biopsy, the patient was treated with antioxidants, vitamins, minerals, and 2% minoxidil. He was also advised to reduce phone use and switch to a hands-free device. The treatment led to complete hair regrowth within four months. The report highlighted the possibility that cell phone radiation could induce hair loss by causing DNA damage, generating reactive oxygen species, and disrupting hormones, underscoring the need for preventive strategies and nutritional therapy.





