TLDR The 595-nm pulsed dye laser effectively reduces symptoms of EFFC with minimal side effects.
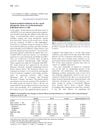
The study reports on the treatment of erythromelanosis follicularis faciei et colli (EFFC) using a 595-nm pulsed dye laser (PDL) in three patients. EFFC is characterized by telangiectasia, hyperpigmentation, and follicular papules, primarily affecting individuals of Asian ancestry. The patients, aged 16, 18, and 27, showed significant improvement in symptoms such as facial erythema and follicular papules after three PDL sessions. Follow-ups ranging from 3 months to 4 years revealed minimal recurrence of symptoms. The study highlights the effectiveness and safety of 595-nm PDL in treating EFFC, though it acknowledges the limitation of a small sample size.
4 citations
,
November 2020 in “Case reports in dermatology” A rare skin condition causes red, dark, bumpy facial lesions.
 14 citations
,
July 2012 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
14 citations
,
July 2012 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Topical tacalcitol ointment can help improve symptoms of EFFC.
11 citations
,
June 2010 in “Dermatologic surgery” The dual-wavelength laser system effectively reduces EFFC symptoms with minimal side effects.
25 citations
,
April 2008 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology” EFFC might be common but underreported.
21 citations
,
August 1991 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” A rare skin condition was found in a young white girl for the first time.
 14 citations
,
July 2012 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
14 citations
,
July 2012 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Topical tacalcitol ointment can help improve symptoms of EFFC.
11 citations
,
June 2010 in “Dermatologic surgery” The dual-wavelength laser system effectively reduces EFFC symptoms with minimal side effects.
10 citations
,
September 1994 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Three Iranian men had reddish-brown facial pigmentation with no effective treatment.