Drug-Induced Postinfantile Giant Cell Hepatitis
October 2010
in “
Hepatology
”
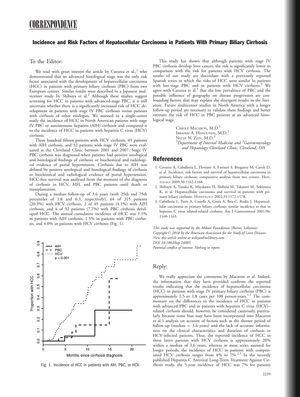
TLDR Certain liver diseases respond well to specific treatments and have varying risks for liver cancer.
The document covered multiple studies and case reports related to liver diseases. One study compared the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) among patients with different types of cirrhosis, finding that those with stage IV primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) had a lower risk of HCC compared to hepatitis C virus (HCV) cirrhosis patients. Another systematic review found peginterferon alfa-2a to be more effective than peginterferon alfa-2b in treating chronic hepatitis C. A case report described a 38-year-old woman with postinfantile giant cell hepatitis (PGCH) linked to Pil-Food, which responded well to corticosteroid and azathioprine therapy. Additionally, drug-induced autoimmune hepatitis (DIAIH) caused by anti-TNF-α agents showed a favorable prognosis with immunosuppressive treatment. Lastly, a study in India identified nonalcoholic fatty liver (NAFL) as a significant cause of cryptogenic cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma, associated with metabolic risk factors.




