BCG'osis
February 1981
in “
Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine
”
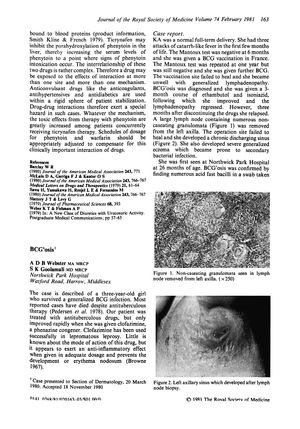
TLDR A three-year-old girl survived a rare serious infection caused by BCG vaccination, which improved after treatment with a leprosy drug.
The document reports the case of a three-year-old girl who survived a generalized BCG infection, a rare complication following BCG vaccination. Initially, the girl presented with a non-healing vaccination site, unwellness, and generalized lymphadenopathy. Despite treatment with standard antituberculous drugs, she relapsed after initial improvement. The infection was confirmed by the presence of acid-fast bacilli in a swab from an axillary sinus and was sensitive to antituberculous drugs. The patient's condition only improved rapidly after the administration of clofazimine, a drug typically used for lepromatous leprosy. The patient also developed severe generalized eczema and alopecia totalis, which was considered to be telogen effluvium triggered by her condition and treatments. The patient's hair regrew after the continuation of antituberculous therapy, and her liver size normalized after discontinuing clofazimine. The case highlights the potential for a rare but serious complication of BCG vaccination and the effectiveness of clofazimine in treating this condition.




