Topical and intralesional therapies for alopecia areata
May 2011
in “Dermatologic therapy”

TLDR No treatments fully cure or prevent alopecia areata; some help but have side effects or need more research.
The document reviewed treatments for alopecia areata (AA), indicating that while there are various options, none are curative or preventive. Topical corticosteroids have limited efficacy and potential side effects like skin atrophy. Intralesional corticosteroids are effective for patchy AA but should be limited to 20 mg per session to avoid side effects. Minoxidil is dose-responsive but not fully understood and can cause contact dermatitis. Anthralin is effective but can cause irritation and staining, while DPCP has a 50-60% success rate but risks severe dermatitis. Latanoprost showed a 45% response rate for eyelash AA, and bimatoprost helped those with less extensive loss. Phototherapy is not favored due to cancer risks, though the 308-nm excimer laser showed a 41.5% regrowth rate. Bexarotene and capsaicin ointment are promising but need more research. Topical tacrolimus, pimecrolimus, imiquimod, and photodynamic therapy were ineffective. The document recommends topical and intralesional corticosteroids for localized AA and contact immunotherapy for extensive cases.
View this study on onlinelibrary.wiley.com →
Cited in this study

research Latanoprost in the treatment of eyelash alopecia in alopecia areata universalis
Latanoprost can effectively treat eyelash hair loss, with 45% of patients showing hair regrowth and no reported side effects.
research Alopecia areata update
The document says current treatments for alopecia areata do not cure or prevent it, and it's hard to judge their effectiveness due to spontaneous remission and lack of studies.

research Alopecia areata update
Half of people with Alopecia Areata may see hair regrowth within a year without treatment, but recovery is unpredictable.

research The efficacy of latanoprost in the treatment of alopecia areata of eyelashes and eyebrows
Latanoprost, a glaucoma treatment, was found ineffective in treating hair loss in eyebrows and eyelashes.
research Phase I/II randomized bilateral half-head comparison of topical bexarotene 1% gel for alopecia areata
Topical bexarotene 1% gel might help regrow hair in alopecia areata and is generally safe.
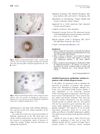
research Instilled bimatoprost ophthalmic solution in patients with eyelash alopecia areata
Bimatoprost is safe but not effective for severe eyelash loss from alopecia areata, possibly helping those with less loss.
research 308‐nm Excimer Laser for the Treatment of Alopecia Areata in Children

research Lack of efficacy of topical latanoprost and bimatoprost ophthalmic solutions in promoting eyelash growth in patients with alopecia areata
Topical latanoprost and bimatoprost eye solutions don't help eyelash growth in people with alopecia areata.
research Alopecia Areata: Evidence-Based Treatments

research Interventions for alopecia areata
Current treatments for alopecia show no significant long-term benefits.

research Lack of response of alopecia areata to pimecrolimus cream
Pimecrolimus cream is not effective for treating alopecia areata.

research Changes in distribution pattern of CD8 lymphocytes in the scalp in alopecia areata during treatment with diphencyprone
Diphencyprone treatment increases CD8 lymphocytes in the scalp, which is associated with hair regrowth in alopecia areata patients.

research Alopecia areata
Alopecia areata causes hair loss, has no cure, and various treatments exist.

research Lack of efficacy of topical latanoprost in the treatment of eyebrow alopecia areata
Topical latanoprost doesn't effectively regrow hair in severe eyebrow alopecia areata cases.
research Influence of prostaglandin F2α and its analogues on hair regrowth and follicular melanogenesis in a murine model
Prostaglandin F2alpha and related compounds can increase hair growth and darken hair in mice.

research Comparison of Azelaic Acid and Anthralin for the Therapy of Patchy Alopecia Areata
Azelaic acid and anthralin are similarly effective for treating patchy hair loss.

research Hypertrichosis of the eyelashes caused by bimatoprost
Bimatoprost can cause excessive eyelash growth.

research Acquired trichomegaly of the eyelashes and hypertrichosis induced by bimatoprost
Bimatoprost can cause longer, thicker, darker eyelashes and eyebrows.
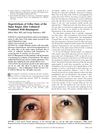
research Hypertrichosis of vellus hairs of the malar region after unilateral treatment with bimatoprost
Using bimatoprost on one side of the face caused increased cheek hair growth in a patient.

research A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of 5% and 2% topical minoxidil solutions in the treatment of female pattern hair loss
5% and 2% minoxidil solutions effectively promote hair growth and reduce hair loss, with 5% being slightly more effective but having more side effects.

research Minoxidil: mechanisms of action on hair growth
Minoxidil boosts hair growth by opening potassium channels and increasing cell activity.

research Restoration of hair growth in mice with an alopecia areata-like disease using topical anthralin
Topical anthralin helped regrow hair in mice with a condition similar to human alopecia.

research Guidelines for the management of alopecia areata
The 2003 guidelines suggest that while some treatments can regrow hair in alopecia areata, none alter the disease's progression, and wigs may be the best option for extensive hair loss.

research Clobetasol propionate 0.05% under occlusion in the treatment of alopecia totalis/universalis
Clobetasol propionate ointment can help some people with total hair loss regrow hair.

research Efficacy of betamethasone valerate foam formulation in comparison with betamethasone dipropionate lotion in the treatment of mild‐to‐moderate alopecia areata: A multicenter, prospective, randomized, controlled, investigator‐blinded trial
Betamethasone valerate foam is more effective and safe for treating mild-to-moderate alopecia areata than betamethasone dipropionate lotion.

research Topical Tacrolimus (FK506): Treatment Failure in Four Cases of Alopecia Universalis

research A randomized clinical trial of 5% topical minoxidil versus 2% topical minoxidil and placebo in the treatment of androgenetic alopecia in men
5% minoxidil works better for hair growth and density, with minor irritation.

research Alopecia areata update
Despite progress in treatment, the exact cause of Alopecia areata is still unknown.

research HAIR REGROWTH
Finasteride and minoxidil are effective for hair regrowth, while treatments for alopecia areata have varying success and continuous treatment is necessary.

research Minoxidil upregulates the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in human hair dermal papilla cells
Minoxidil boosts growth factor in hair cells, potentially promoting hair growth.
research PUVA treatment of alopecia areata partialis, totalis and universalis: audit of 10 years' experience at St John's Institute of Dermatology
research Treatment-resistant alopecia areata. Response to combination therapy with minoxidil plus anthralin
Using minoxidil and anthralin together can improve hair regrowth in severe alopecia areata patients who didn't respond to individual treatments.

research The Effect of Topical Minoxidil on Hair Follicular Cycles of Rats
Minoxidil speeds up hair growth in rats without prolonging growth phase.

research Alterations in scalp blood flow after the epicutaneous application of 3% minoxidil and 0.1% hexyl nicotinate in alopecia
Minoxidil didn't increase scalp blood flow for hair growth, but hexyl nicotinate did.

research Topical minoxidil solution (1% and 5%) in the treatment of alopecia areata
Minoxidil solution helps hair regrowth in alopecia areata, with 5% being more effective.

research Action of topical minoxidil in the bald stump-tailed macaque
Minoxidil promotes hair growth but stops working when discontinued.

research Double-blind, placebo-controlled evaluation of topical minoxidil in extensive alopecia areata
Minoxidil helps hair growth in 63.6% of alopecia patients, with 27.3% having excellent results.

research Minoxidil Stimulates Cutaneous Blood Flow in Human Balding Scalps: Pharmacodynamics Measured by Laser Doppler Velocimetry and Photopulse Plethysmography
Minoxidil increases blood flow in balding scalps, possibly reversing hair loss.
Related
research Hair and Nail Conditions: Alopecia Evaluation
Alopecia causes hair loss and should be treated early, especially scarring types where hair cannot regrow.

research A clinico-epidemiological study of scalp hair loss in children (0–18 years) in Kota Region, South-East Rajasthan
About 12% of children in Kota, Rajasthan, experience hair loss, mainly due to fungal infections, with early treatment advised to prevent worsening.
research Treating of resistant cases of alopecia universalis
Combining platelet-rich plasma therapy with prostaglandin-F eye drops can significantly regrow hair in alopecia universalis.

research Topical and intralesional therapies for alopecia areata
No treatments fully cure or prevent alopecia areata; some help but have side effects or need more research.

research Acquired scalp alopecia. Part I: A review
Accurate diagnosis is key for treating different kinds of hair loss, and immune response variations may affect the condition and treatment results.