Cutaneous Mastocytosis Associated With Congenital Alopecia
July 2012
in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
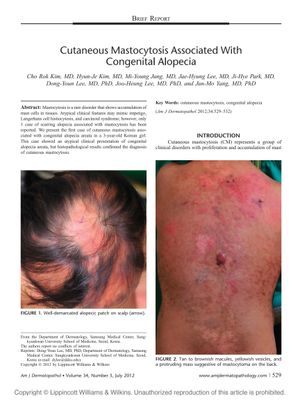
TLDR A 3-year-old girl with skin mast cell buildup and congenital baldness improved with treatment, suggesting a rare link between these conditions.
The document reports the first case of cutaneous mastocytosis (CM) associated with congenital alopecia areata (AA) in a 3-year-old Korean girl. CM is characterized by the accumulation of mast cells in the skin and can present in various forms, including urticaria pigmentosa, which was observed in this case. The girl was born with an absence of scalp hair and developed well-demarcated bald patches with pigmented hair growth around them. Histological examination confirmed the diagnosis of CM. The patient's CM and associated alopecia showed improvement after 9 months of treatment with topical hydrocortisone and oral antihistamines. The case suggests that severe mastocytosis can cause inflammation of hair-bearing skin and be a rare cause of alopecia, particularly in young children. The document also discusses the potential association between alopecia and mast cell disease, noting that mast cell granules contain cytokines and growth factors that may affect hair follicle development and cycling. It is suggested that further studies are needed to understand the mechanism of alopecia associated with systemic mastocytosis.
View this study on journals.lww.com →
Cited in this study

research Potential Involvement of the Stem Cell Factor Receptor c-kit in Alopecia Areata and Androgenetic Alopecia: Histopathological, Immunohistochemical, and Semiquantitative Investigations
c-kit affects hair growth and color in alopecia areata and androgenetic alopecia.